![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
draw and label a nerve cell and its components |
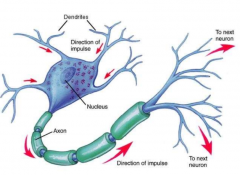
cell body, dendrites, axons, myelin, direction of impulse |
|
|
what does Nissl substance do |
cell stain, especially for rough ER |
|
|
what are the 3 major types of neuronal types and their characteristics, as well as the type of cell they innervate |
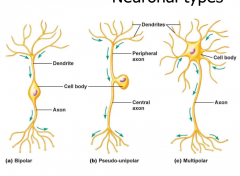
multipolar: cell body attached to dendrites, long axon. most vertebrate neurons. pseudo-unipolar: dendrites to peripheral axon to single branch to body, to axon. dorsal root ganglion bipolar: dentrite to central cell body to axon. retina, olfactory epithelium unipolar? |
|
|
define the neuron doctrine |
theory developed by ramon y cajal that neurons communicate with synapses, not physical connections |
|
|
list and describe the types of cell-cell interactions |
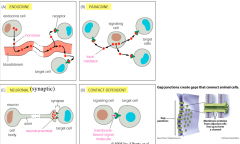
endocrine: hormones, long distance paracrine: chemical, local release neurotransmitter: synapse contact dependent: membrane bound target and receptor gap junctions: connections between cells for direct flow of substances |
|
|
describe synaptic transmission |
action potential arrives in synapse, calcium and sodium influx, vesicles move to membrane and release neurotransmitter, receptor across synaptic cleft receives target and propagates action potential. neurotransmitter is broken down and reuptaken |
|
|
define afferent |
flow of information/signal to the cell body (usually from dendrites) |
|
|
define efferent |
flow of information/signal away from cell body (usually to axon terminal) (E Exit)
|
|
|
define retrograde |
flow of chemicals/materials to back to the cell body
|
|
|
define anterograde |
flow of chemicals/materials away from cell body |
|
|
what are they two general terms for major types of glia |
microglia and macroglia |
|
|
describe microglia and their applications |
close cousins of phagocytic immune cells, mainly used in removal of waste/debris/toxins from neurons. useful in development |
|
|
describe macroglia and their applications |
1. myelin forming cells (oligodendrocyte [CNS] and Schwann Cells [PNS]) 2. Supporting cells (Astrocytes [CNS], Satellite cells [PNS]) |
|
|
describe the role of astrocyte (glial cell) in a synaptic cleft |
surrounds synaptic cleft, acts as storage, breakdown of neurotransmitters absorbed, respond to neurotransmitter, act as bridge to blood-brain barrier tripartite synapse (integral part of synapse) |
|
|
describe myelin and its role in nerve transduction |
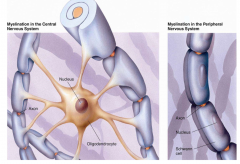
myelin is the product of myelin forming cells (Schwann cells in the PNS, oligodendrocytes in CNS) that acts as an insulating coating around an axon and propagates/amplifies an action potential with saltation, at nodes of ranvier Schwann cell bodies are inside myelin sheath (schwann cell cytoplasm can wrap multiple axons for protection but not same as myelin), oligodendrocyte bodies are outside and provide myelin to multiple axons |
|
|
what is multiple sclerosis |
degenerative disease (usually autoimmune) where myelin is lost/destroyed, loss of signal propagation and function. no treatment, only slow progress of disease |
|
|
in the process of neuralation, what guides the ectoderm neural plate cells to form the neural groove and eventually neural fold |
inductive signals from bone morphogenic proteins and sonic hedgehog proteins (released from notochord and developing neural tube itself) with concentration gradients |
|
|
describe neuralepithelial cells and their development |
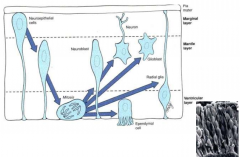
initially they extend the length of the membrane up to the pia matter (premature brain), when they are ready to become more advanced they shrink down to the bottom to enter into mitosis and differentiate into various neural cell types from there |
|
|
what is the primary function of radial glia |
guiding neurons up to the surface as they develop. later developing cells usually need to move further up |
|
|
how is regionalization achieved
|
homeobox (HOX) genes which are highly conserved throughout nature. forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, spinal cord and their subdivisisions |
|
|
what are the names for clusters of cells in each nervous system |
central: nucleus (nuclei) peripheral: ganglion (ganglia) |
|
|
what is the difference between white and gray matter in the brain/spinal cord |
white: myelinated gray: unmylinated |
|
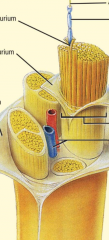
label this peripheral nerve |
locate axon, mylin sheath, endoneurium (surround axon), perineurium (surround axon group) and fascicle (axon group) blood vessels epineurium (surround nerve trunk) |
|
|
describe the enteric nervous system
|
neuronal network in the gut, allow muscles to contract and release of chemicals for digestion typically use seratonin as a neurotransmitter, SSRI treatments usually have gastrointestinal side effects |

