![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 2 things bones are mostly made of? |
Cells, Extracellular Matrix (ECM) |
|
|
What is the ECM made of? |
-Minerals: (calcium, phosphate) make the bone hard -Proteins : (collagen!!) makes bones flexible |
|
|
What happens to bones when you remove the organic matrix? |
Bone without it’s organic matrix (collagen) is brittle and shatters easily. |
|
|
What happens to bones when you remove its inorganic matrix? |
Bone without it’s inorganic matrix (minerals) can not resist compression |
|
|
What types of cells are in bones? |
1. Osteogentic (stem cell=gives rise to osteoblasts) 2. Osteoblast (matrix-synthesizing call responsible for bone growth) 3. Osteocyte (mature bone cell that monitors and maintains the mineralized bone matrix) (an osteocyte is an osteoblast cell trapped in an ECM) (strain sensor for bone, can trigger bone formation OR resorption) 1-3 work together!!^^^^ 4. Osteoclast (bone-resorbing cell) (break down bone) |
|
|
How do osteoblasts and osteoclasts work with calcium? |
Osteoblasts remove calcium from blood and into the bone
Osteoclasts remove calcium from bones and into the blood |
|
|
What are the 5 bone classifications based on shape? |
1. Long bone- longer than it is wide (ex. Humerus) 2. Short bone- bone is about as long as it is wide (ex. Trapezium) 3. Flat bone- bone is broad, flat and thin (ex. Sternum) 4. Irregular bone- bone fits in no class (ex. Vertebra) 5.Sesamoid bone- bone is round and flat (ex. Patella) |
|
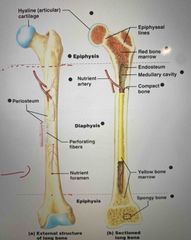
Front (Term) |
Remember info on Diaphysis, Epiphysis, Periosteum, Spongy bone, Red bone marrow, medullary cavity, articular cartilage (bone video #1 16:20) |
|
|
2 types of bones |
Spongy bone (also known as tranecular bone)- on inside Compact bone- on outside |
|
|
Locations of bone marrow |
Red bone marrow is the source of blood cell formation Child- Medullary cavity of long bones, spaces in spongy bone Adult- Medullary cavity red marrow turns to yellow marrow (fat) Summary - child has no yellow marrow, adult has yellow marrow in long bones |
|
|
Read bone marrow transplantation on p. 187 |
|

