![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
120 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. Fertilization normally occurs within which structure?
|
b) Fallopian tube
|
|
|
2. This is a series of functional changes that sperm go through when they are in the female reproductive tract.
|
d) Capacitation
|
|
|
3. The fusion of the secondary oocyte and the sperm results in which developmental stage?
|
c) Zygote
|
|
|
4. This is the part of the blastocyst that promotes implantation and produces hCG.
|
c) Trophoblast
|
|
|
5. This is the portion of the endometrium that lies between the embryo and the stratum basalis.
|
a) Decidua basalis
|
|
|
6. This develops from the epiblast and carries a protective fluid.
|
d) Amnion
|
|
|
7. This will become the primary structure for exchange of material between the mother and the fetus.
|
a) Chorionic villi of the placenta
|
|
|
10. How many pairs of pharyngeal arches are there?
|
e) 6
|
|
|
8. Each somite may differentiate into a
|
b) Dermatome
|
|
|
9. This is the connection between the placenta and the embryo.
|
c) Umbilical cord
|
|
|
11. This is any agent or influence that causes developmental defects in an embryo.
|
e) None of the above
|
|
|
12. This exam is performed between 14-16 weeks gestation and is used to detect genetic abnormalities.
|
b) Amniocentesis
|
|
|
13. CVS is taking cells from where?
|
c) Placenta
|
|
|
14. This hormone is secreted by nonpregnant women from secretory cells in the hypothalamus.
|
c) CRH
|
|
|
15. During pregnancy stroke volume can increase by
|
c) 30%
|
|
|
16. Labor can not take place until all of this hormone’s effects are diminished.
|
b) Progesterone
|
|
|
17. This is the time from the onset of labor to the complete dilation of the cervix.
|
a) Stage of dilation
|
|
|
18. Involution is
|
c) When the uterus decreases in size
|
|
|
19. In infants this connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava.
|
a) Ductus venosus
|
|
|
20. This is a principle hormone that releases milk into the mammary ducts.
|
d) Oxytocin
|
|
|
21. This is a permanent change in an allele.
|
a) Mutation
|
|
|
22. When phenotype can be drastically different depending on parental origin it is called:
|
c) Genomic imprinting
|
|
|
23. An example of incomplete dominance is
|
b) Sickle-cell disease
|
|
|
24. If one parent has type A blood and one parent has type B blood, what blood type is possible for their child?
|
e) All of the above
|
|
|
25. If a child has B blood, and the mother has B blood, what is the possible genotype of the father?
|
e) B, O or AB
|
|
|
26. Chromosome #15 is considered
|
b) An autosome
|
|
|
27. A Barr body
|
a) Is an inactivated X chromosome
|
|
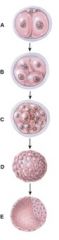
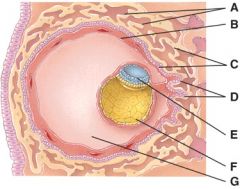
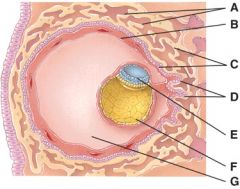
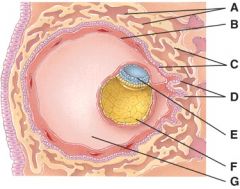
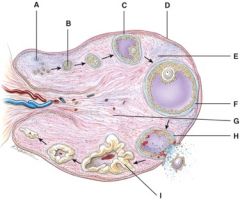
28. Which one represents the morula stage?
|
c) C
|
|
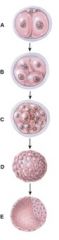
29. Which one represents the blastocyst stage?
|
D
|
|
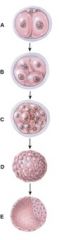
30. What does diagram “A” represent?
|
b) Cleavage of zygote
|
|
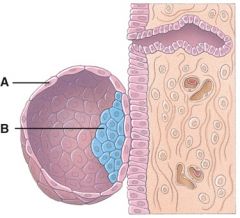
31. What is line “A” pointing to?
|
b) Trophoblast
|
|
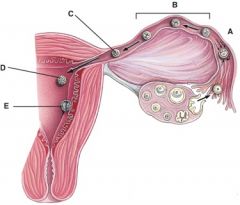
32. What stage happens 3-4 days after fertilization?
|
C
|
|
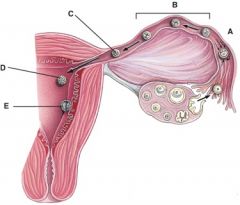
33. What stage happens 6 days after fertilization?
|
E
|
|
34. This was formerly called the blastocyst cavity.
|
F
|
|
35. This is composed of the syncytiotrophoblast and the cytotrophoblast.
|
C
|
|
36. Where is the amnion?
|
E
|
|
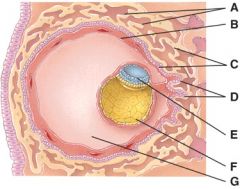
37. These cells are derived from the yolk sac and form a connective tissue layer.
|
F
|
|
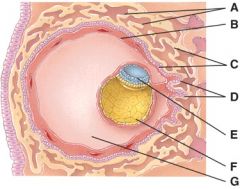
38. What is line “G” pointing to?
|
e) None of the above
|
|
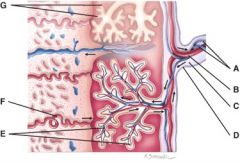
39. What is line “G” pointing to?
|
a) chorionic villi
|
|
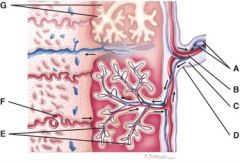
40. Where are the fetal blood vessels?
|
E
|
|
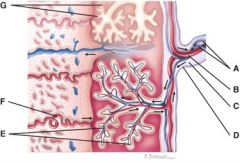
41. What is line “F” pointing to?
|
d) maternal endometrial layer
|
|
|
1. The structure protects and regulates the temperature of the testes
|
d) Scrotum
|
|
|
2. This structure is the site of sperm production.
|
b) Seminiferous tubules
|
|
|
3. How many seminiferous tubules are found in the lobules?
|
a) 1-3
|
|
|
4. These cells may eventually become spermatozoa
|
c) Spermatogenic cells
|
|
|
5. These cells secrete testosterone.
|
c) Leydig cells
|
|
|
6. This hormone stimulates Leydig cells to secrete testosterone.
|
b) LH
|
|
|
7. The straight tubules in the testis lead into the:
|
c) Rete testis
|
|
|
8. The function of the epididymis is
|
a) Sperm maturation
|
|
|
9. This is formed by the union of the duct from the seminal vesicle and the ampulla of the vas deferens.
|
d) Ejaculatory duct
|
|
|
10. This lies posterior to the bladder and anterior to the rectum and secretes an alkaline, fructose filled fluid.
|
c) Seminal glands
|
|
|
11. These are located inferior to the prostate on other side of the membranous urethra within the deep muscles of the perineum.
|
a) Cowper’s glands
|
|
|
12. This is composed of three cylindrical masses of erectile tissue each surrounded by a fibrous tissue.
|
d) Penis
|
|
|
13. This ligament arises from the pubic symphysis in males.
|
c) Suspensory ligament
|
|
|
14. What is produced by the ovaries?
|
d) Secondary oocytes, estrogen and progesterone
|
|
|
15. This attaches the ovaries and the uterus to the pelvic wall.
|
d) Suspensory ligament
|
|
|
16. This is the site of fertilization.
|
c) Uterine tubes
|
|
|
17. This is the portion of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
|
b) Cervix
|
|
|
18. Anterior to the vagina and urethral openings is the
|
d) Cervical sphincter
|
|
|
19. Skene’s glands secrete
|
e) Mucus
|
|
|
20. ________ hormone secreted by the ____________ controls the ovarian and uterine cycles.
|
c) GnRH, hypothalamus
|
|
|
21. This hormone promotes spermatogenesis.
|
b) Testosterone
|
|
|
22. This hormone triggers ovulation.
|
b) LH
|
|
|
23. This is secreted by the corpus luteum after ovulation.
|
a) Progesterone
|
|
|
24. The is the uterine phase when the endometrium becomes more vascular.
|
c) Proliferative phase
|
|
|
25. The is the ovarian phase between the end of menstruation and beginning of ovulation.
|
b) Preovulatory phase
|
|
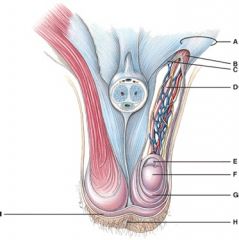
26. The septum of the tissue is made up of superficial fascia and which muscle tissue?
|
I
|
|
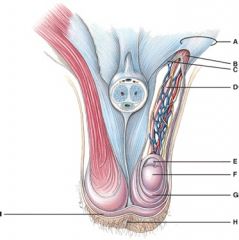
27. What does line “A” point to?
|
d) Spermatic cord
|
|
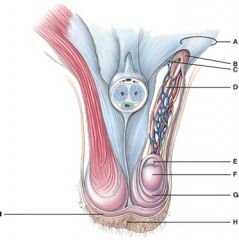
28. Which structure has a portion removed in a vasectomy?
|
D
|
|
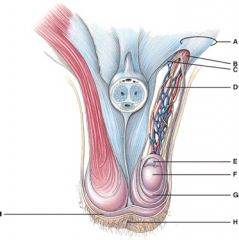
29. What does line “G” point to?
|
e) Tunica vaginalis?
|
|
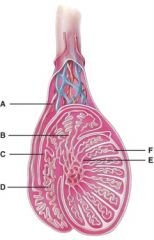
30. What is line “C” pointing to?
|
b) Rete testis
|
|
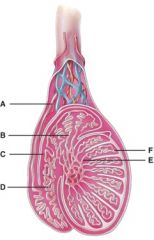
31. Where are the straight tubules?
|
e) E
|
|
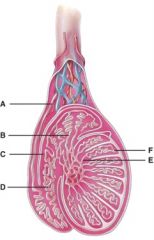
32. What is line “F” pointing to?
|
e) Seminiferous tubules
|
|
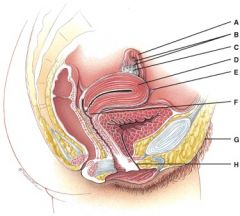
34. What is line “C” pointing to?
|
c) Ovary
|
|
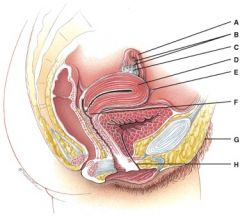
36. This opens from the uterus to the vagina.
|
F
|
|
37. This consists of primary oocyte that is surrounded by several layers of cuboidal granulosa cells.
|
B
|
|
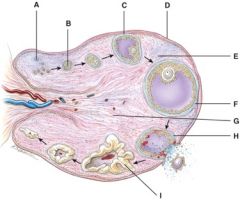
38. Where is the mature (graafian) follicle?
|
F
|
|
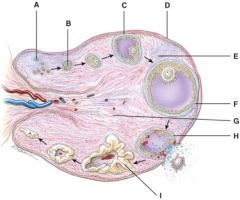
39. Where is the corpus albicans?
|
e) None of the above
|
|
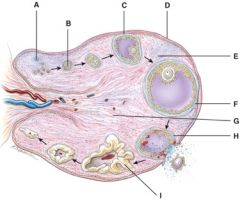
40. This will produce progesterone, estrogens, relaxin and inhibin.
|
I
|
|
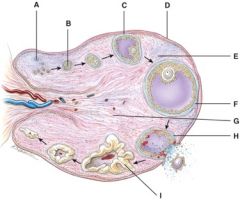
41. What is line “D” pointing to?
|
b) Germinal epithelium
|
|
|
1. Which of the following is NOT a function of a hormone?
|
d. Produces electrolytes
|
|
|
2. When a hormone is present in excessive levels, the number of target-cell receptors may decrease. This is called:
|
e. Down regulation
|
|
|
3. These hormones act on neighboring cells without entering the bloodstream.
|
e. All of the above
|
|
|
4. These are lipid soluble hormones derived from cholesterol.
|
a. Steroids
|
|
|
5. Which of the following is a major eicosanoid?
|
d. Both a and b
|
|
|
6. What is a major difference in the action of a water soluble hormone versus a lipid soluble hormone?
|
c. The use of a second messenger
|
|
|
7. When one hormone opposing the action of another hormone is it called:
|
c. Antagonistic effects
|
|
|
8. Which of the following is not a way hormone secretion is regulated.
|
c. C. Signals from the peripheral nervous system
|
|
|
9. What controls the anterior pituitary gland?
|
c. Action of hypothalamic hormones
|
|
|
10. Which of the following anterior pituitary hormones stimulates growth.
|
a. Human growth hormone
|
|
|
11. Which of the following anterior pituitary hormones stimulates milk production.
|
b. Prolactin
|
|
|
12. Which of the following anterior pituitary hormones stimulates Cortisol production.
|
e. Adrenocorticotropic hormone
|
|
|
13. Which of the following anterior pituitary hormones stimulates sex cell production.
|
a. Leutinizing hormone
|
|
|
14. The pars distalis and the pars tuberalis comprise:
|
a. The anterior pituitary
|
|
|
15. How many hormones do the five types of anterior pituitary cells secrete?
|
b. 7
|
|
|
16. Which type of anterior pituitary cell secretes human growth hormone?
|
c. Somatotrophs
|
|
|
17. Which hormones does the posterior pituitary produce?
|
c. Oxytocin and Antidiruetic hormone
|
|
|
18. The amount of ADH that is secreted varies with
|
a. Blood osmotic pressure
|
|
|
19. Which of the following hormones opposes the action of parathyroid hormone?
|
d. Calcitonin
|
|
|
20. Which of the following is not a means of synthesizing and secreting T3 and T4.
|
d. Hydrolysis of calcium
|
|
|
21. Parathyroid hormone is the major regulator of which ions in the blood?
|
a. Calcium
|
|
|
22. Complete loss of the Aldosterone will lead to death due to:
|
c. Dehydration
|
|
|
23. Which of the following is not a glucocorticoid effect?
|
e. Increase in blood cell production
|
|
|
24. Which blood glucose lowering hormone is produced by the pancreatic islet cells?
|
a. Insulin
|
|
|
25. Which hormone is promotes metabolic rate?
|
d. Thyroid hormone
|
|
|
26. Which hormone is stimulated by decreases in blood glucose?
|
c. Glucagon
|
|
|
27. Which of the below hormones is part of the body’s long term response to stress?
|
c. Cortisol, hGH, Thyroid hormone
|
|
|
28. The responses of the body to long term stress does NOT include which one of the following responses.
|
Increased heart rate
|
|
|
29. This is an amine hormone derived from seratonin.
|
a. Melatonin
|
|
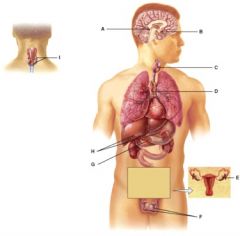
This gland secretes hGH, TSH and FSH among other hormones.
|
B
|
|
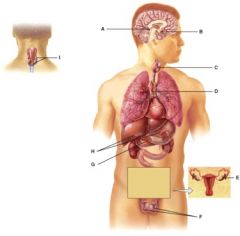
The hormones from this gland help regulate metabolism.
|
C
|
|
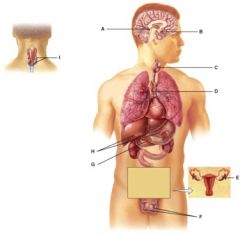
This gland’s hormones help regulate blood calcium levels.
|
I
|
|
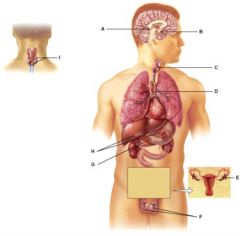
This gland produces stress reducing steroid hormones.
|
H
|
|
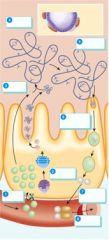
Which step represents the synthesis of TGB?
|
2
|
|
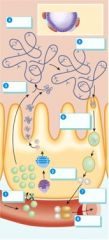
Which step represents coupling of T1 and T2?
|
5
|
|
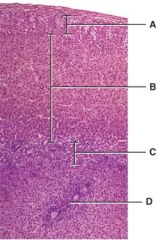
Which level secretes mainly aldosterone?
|
A
|
|
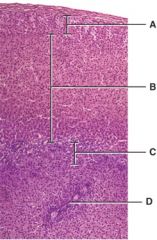
Which layer secretes androgens?
|
C
|
|
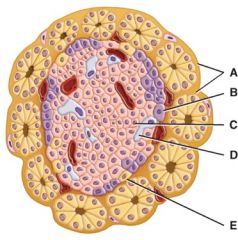
Which cell secretes glucagon?
|
B
|
|
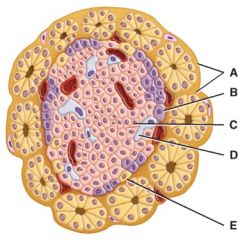
Which cell secretes the blood glucose-reducing hormone?
|
C
|
|
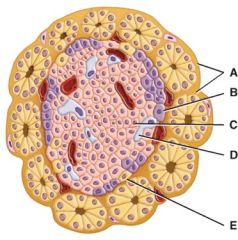
Which cell secretes somatostatin?
|
D
|

