![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Resolving Power |
smallest detectable separation of two points |
|
|
formula for RP |
=wavelength -------------------- 2 x NA |
|
|
compound microscope |
has 2 magnifying lenses |
|
|
why are blue filters used between the light source and condenser? |
because blue light improves resolution |
|
|
parcentric: |
specimen will be centered when objective lenses are switched |
|
|
parfocal: |
all objective lenses will be easy to focus |
|
|
which is not an optical part? -ocular lenses -iris diaphragm -objective lenses |
iris diaphragm |
|
|
worst color of light to use for distinguishing between 2 microorganisms on Brightfield microscopes? |
red |
|
|
why don't you use old cultures for Gram staining procedure? |
they don't retain the primary stain as well as new cultures |
|
|
function of broth to grow microorganisms? |
-maintain osmotic conditions -supply nutrients -maintain proper pH |
|
|
why do we use slants? |
it's easier to store bacteria |
|
|
contamination: |
unintentionally introducing bacteria to media |
|
|
procedure of Gram staining: |
1. smear and air dry and heat fix on slide 2. crystal violet & 60 sec 3. rinse with water 4. iodine & 60 sec 5. acetone rinse (decolorizer) & few sec 6. rinse immediately 7. counterstain (safranin) & 60 sec 8. rinse and dry blot |
|
|
Gram staining: what color do Gram-positive cells turn? |
purple |
|
|
Gram staining: what color do Gram-negative cells turn? |
pink |
|
|
primary stain |
stain that is used to color the "target" cells |
|
|
mordant |
a chemical that react with the primary stain and with the cell you want to see |
|
|
counterstain |
usually a simple stain to color everything that wasn't stained by the primary color |
|
|
procedure of Endospore staining/Schaeffer-Fulton method: |
1. smear and air dry and heat fix on slide 2. piece of paper on slide 3. soak with malachite green & 60 sec 4. heat 5. repeat 3 & 4 for 5 min 6. rinse 7. counterstain (safranin) & 30-60 sec 8. rinse and blot |
|
|
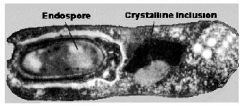
types of endospores: Clostridium tetani-tetanus Clostridium perfringens-food poisoning Clostridium difficile-diarrhea Clostridium botulinum-botulism |
*club shaped |
|
|
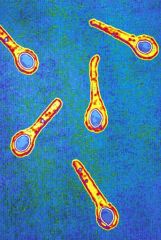
types of endospores: Bacillus thuringiensis |
*terminal with crystal shaped inclusion |
|
|
types of endospores: Bacillus cereus Bacillus subtilis Bacillus anthracis |
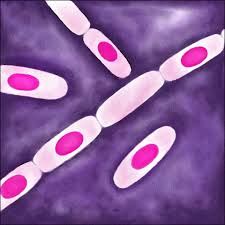
*centered |
|
|
obligate aerobes: |

only grow in air |
|
|
facultative anaerobes: |

grow in presence or absence of oxygen |
|
|
aerotolerant anaerobes: |

will grow in oxygen but better with no oxygen |
|
|
microaerophiles: |

grow in a reduced oxygen concentration |
|
|
obligate anaerobes: |
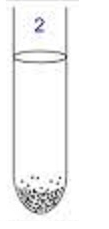
only grow in absence of oxygen, poisoned by oxygen |
|
|
bacteriostatic |
antibiotics that inhibit growth of microorganisms |
|
|
bactericidal |
antibiotics that kill microorganisms |
|
|
how effective is rubbing the skin with an alcohol swab at removing bacteria? |
-alcohols can coagulate proteins (denature) at concentrations of 50-70% -dissolve lipid membranes, disrupting bacterial structure |
|
|
why are bacteria becoming more resistant to antibiotics? |
because they share plasmids that contain information to do so |
|
|
inoculation: |
intentionally introducing bacteria to media |
|
|
how does penicillin inhibit bacterial growth? |
inhibits cell wall synthesis |
|
|
turbidity: |
measure of a liquid's clarity |
|
|
what are patients given as antibiotics? |
transient flora |
|
|
tetracycline: |
inhibits bacterial growth by inhibiting ribosomes and protein synthesis |
|
|
objective of streak plate method? |
to obtain separate colonies |
|
|
how are antibiotics made? |
by other microorganisms as they compete for food |
|
|
where do you find Staph aureus? |
upper nares |
|
|
where do you find Staph mutans? |
oral cavity |
|
|
pyelonephritis: |
severe UTI |
|
|
cystitis |
infection of lower urinary track and bladder |
|
|
type of blood used in blood agar? |
ovine |
|
|
narrow spectrum antibiotics: |
antibiotics that work against only certain bacteria |
|
|
broad spectrum antibiotics: |
antibiotics that work against wide range of disease causing bacteria |
|
|
1 ml = ____ microliters |
1000 |
|
|
gamma-hemolysis: |
-no hemolytic action by microorganism -good |
|
|
alpha-hemolysis: |
-incomplete hemolysis because RBCs are not completely lysed (pokes holes in RBCs) -greenish zone -okay
|
|
|
beta-hemolysis: |
-complete lysis of RBCs -colonies=clear or straw color -bad! |
|
|
m Endo MF agar |
-tests water with membrane papers -selective (for Gram-) and differential (for lactose fermenting) membrane -incubate at 37*C for 24 hrs -lactose non-fermenters=clear, colorless colonies -lactose fermenters= red to black with golden metallic sheen |
|
|
action limit for water: |
4 coliforms per 100mL |
|
|
MPN: |
number of coliforms present per 100 mL of water |
|
|
Nutrient agar |
-no nutritional value -incubate at 37*C for 24-36 hrs |
|
|
Kirby-Bauer method |
-on Mueller-Hinton agar -filter paper discs -incubate at 37*C for 16-18 hrs |
|
|
MacConkey agar |
-contains bile salts and crystal violet dye -selective and differential for Gram - bacteria -for urine samples -incubate at 37*C for 24 hrs -acid from lactose fermentation=red/pink colonies (E.coli) -non-lactose fermenting metabolize peptone=colorless colonies (salmonella, proteus) |
|
|
blood agar |
-detects growth of most organisms -incubate at 37*C |
|
|
Phenol Red mannitol salts |
-contains 7.5% NaCl -incubate at 37*C for 48 hrs -bad colonies=golden color w/ yellow zone |
|
|
S. aureus and S. epidermidis on PRMS plate forms what? |
large golden yellow colonies with yellow zone |
|
|
will E. coli grow after incubation on petri plate with water and agar? |
no |
|
|
gelatin=? agar=? |
gelatin=protein agar=polysaccharide |
|
|
Virulence factors: |
molecules produced by pathogens and contribute to the pathogenicity of the organism that enable them to achieve the following |
|
|
what environmental factors influence the efficacy of a disinfectant or antiseptic? |
-presence of organic matter -temperature -pH -kind of microorganisms present |
|
|
hemolysins |
enzymes that lyse RBCs |
|
|
leukocidins |
lysis of leukocytes with resultant leukopenia |
|
|
coagulase |
catalyzes conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin with resultant clot formation |
|
|
fibrinolysin |
catalyzes conversion of plasminogen to fibrinolytic enzyme plasmin |
|
|
lipase |
allow bacteria to penetrate fatty tissue with consequent formation of abscesses |
|
|
IgA protease |
bacteria that colonize mucous membranes produce IgA protease which degrades secretory IgA |
|
|
collagenase |
catalyzes degradation of collagen |
|
|
hyaluronidase |
aka spreading factor -catalyzes breakdown of hyaluronic acid, allows bacterial cells to spread through tissue |

