![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a monosaccharide? |
A carbohydrate made up of a single sugar |
|
|
What is another name for monosaccharides? |
Simple sugars |
|
|
What is a disaccharide? |
A carbohydrate made up of 2 monosaccharides (sugars) |
|
|
In a disaccharide, there is 1 _____ bond |
Glycosidic (acetal) bond |
|
|
What is an oligosaccharide? |
A short chain of simple sugars |
|
|
What is another name for oligosaccharides? |
Dextrins |
|
|
What are polysaccharides? |
A long chain of simple sugars |
|
|
What is another name for polysaccharides? |
Dextrans |
|
|
An aldose is a sugar that contains an... |
...aldehyde |
|
|
A ketose is a sugar that contains a... |
...ketone |
|
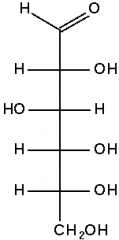
What is the name of this monosaccharide? |
Glucose |
|
|
What category of monosaccharides does glucose fall under? |
Aldoses |
|
|
What category of monosaccharides does fructose fall under? |
Ketoses |
|
|
Most higher organisms use _____ carbohydrates |
D |
|
|
An aldehyde plus an alcohol creates a... |
...hemiacetal |
|
|
Why does a hemiacetal form a ring? |
To stabilize itself |
|
|
In glucose, if the -OH is facing downward, it is denoted as... |
...alpha-glucose |
|
|
In glucose, if the -OH is facing upward, it is denoted as... |
...beta-glucose |
|
|
Once the monosaccharide forms the ring, the carbon 1 -OH group is now... |
...locked in its position |
|
|
To go from the alpha anomer to the beta anomer, it must first go through the _____ to change |
Linear form |
|
|
When the alpha anomer transitions into the beta anomer, this process is called... |
...mutarotation |
|
|
Galactose's ring structure is very similar to glucose's, but it can be differentiated by... |
...an -OH group that points upward on Carbon 4 |
|
|
When 50 molecules of an aldose and 50 molecules of an alcohol, a hemiacetal temporarily forms, which then forms into an acetal by reacting with the remaining alcohol. How many molecules of the aldose and acetal are there after the reaction? |
25 molecules of aldose and 25 molecules of acetal |
|
|
At any given temperature, the two anomers will be _______ with the linear form. |
In equilibrium |
|
|
How does one differentiate the alpha and beta glycosidic bond? |
The beta glycosidic bond forms a "bow tie" |
|
|
When glucose is reduced, it forms into what? |
It forms into glucitol (sorbitol). That is, it loses the aldehyde. |
|
|
When glucose is oxidized it can form two carboxylic acid compounds. What are they? |
Gluconic acid and glucuronic acid |
|
|
When glucose is oxidized at Carbon 1, it will form what derivative? |
Gluconic acid |
|
|
When glucose is oxidized at Carbon 6, it will form what derivative? |
Glucuronic acid |
|
|
What can glucuronic acid do that gluconic acid can't? |
It can form a hemiacetal bond with itself, producing a ring structure. |
|
|
Dexoy sugars are defined as... |
...monosaccharides that have had one or more -OH groups replaced by a Hydrogen. |
|
|
In a dexoy sugar, the "base" gets attached to what Carbon? |
Carbon 1 |
|
|
In a dexoy sugar, the phosphoester bond forms where? |
Carbon 5 |
|
|
Deoxyribose differs from ribose in that... |
...it has a Hydrogen at Carbon 2 instead of a -OH group |
|
|
Amino sugars contain what? |
An amino group, usually attached at Carbon 2 |
|
|
Glucosamine has what attached at Carbon 2? |
An amine (-NH2) |
|
|
N-acetylgalactosamine has what attached at Carbon 2? |
A acetylamine (-NH2COCH3) |
|
|
What is the structural name for maltose? |
Glucose-alpha (1,4)-glucose |
|
|
Because there is an exposed hemiacetal on the second glucose in maltose, it is called what? |
The reducing end |
|
|
Why do di-, oligo-, and polysaccaharides have to be broken down into monosaccharides? |
Because only the simple sugar is small enough to be moved into the cell. Therefore, multisugar carbohydrates must be broken down to be of use. |
|
|
If multisugar carbohydrates are not immediately, where are they stored? |
In the intestines |
|
|
What is the structural name for sucrose? |
Glucose-alpha (1,4)-fructose |
|
|
What is the common name for sucrose? |
Table sugar |
|
|
Because fructose is a ketose, and therefore contains a ketone, can it be oxidized? |
No. |
|
|
Since fructose cannot be oxidized, it does not form a hemiacetal. Therefore, when sucrose is created it has 2 of what? |
Non-reducing ends. Therefore, sucrose is a non-reducing disaccharide. |
|
|
What is high fructose corn syrup? |
A sucrose with a 40:60 split in glucose and fructose, respectively. |
|
|
Because high fructose corn syrup does not trigger an insulin release, there is no up regulation of GLUT. Because of this, what can be said about blood sugar levels? |
It is increased |
|
|
What is the structural name for lactose? |
Galactose-beta (1,4)-glucose |
|
|
Does lactose have a reducing end? |
Yes |
|
|
If the enzyme lactase is not present, what happens to the ingested lactose? |
It gets broken down by gut microbes |
|
|
What is the structural name of cellbiose? |
Glucose-beta (1,4)-glucose |
|
|
How many monosaccharides make up stachyose? |
4 (i.e. it is a tetrasaccharide) |
|
|
What is the structural name of stachyose? |
Galactose-alpha (1,6)-galactose-alpha (1,6)- glucose-alpha (1,5)-fructose |
|
|
Can mammals digest stachyose? |
No |
|
|
Where can stachyose be found? |
In beans, peas, bran, and whole grains |
|
|
Some oligosaccharides can act as what? |
Anti-biotics |
|
|
What are two oligosaccharides that act as anti-biotics? |
Streptomycin and bleomycin A2 |
|
|
What are glycans? |
Polysaccharide polymers that are put together with acetal linkages. They can be composed of monosaccharides or monosaccharide derivatives. |
|
|
What is the function of a starch? |
It is a polysaccharide that stores carbohydrates |
|
|
What are two common starches? |
Amylose and amylopectin |
|
|
What is amylose a polymer of? |
Glucose |
|
|
What is the basic structure of amylose? |
(glucose-alpha (1,4)-glucose)n, where n is equal to the number of units. |
|
|
Amylose is what kind of polymer? |
A linear polymer |
|
|
In an aqueous environment, what happens to amylose? |
The linear chain curls into a helix. |
|
|
How does amylopectin differ from amylose? |
It is a branching polymer |
|
|
What is the basic structure of amylopectin? |
(glucose-alpha (1,4)-glucose)n with (glucose-alpha (1,6)-glucose)n branches |
|
|
How many sugars can be present in a chain that branches from alpha (1,6)? |
20 to 30 sugars |
|
|
How many sugars can be present in the alpha (1,4) branch? |
25 to 30 sugars |
|
|
What bonds do salivary amylases hyrdolyze? |
The alpha (1,4) bonds |
|
|
What bonds do intestinal amylases/isomaltases hydrolyze? |
The alpha (1.6) bonds |
|
|
There are two factor that differ glycogen from amylopectin, What are they? |
1. the alpha (1,6) branches are closer together. 2. there is a glycogenin protein at the center of the polysaccharide |
|
|
To begin the initial elongation, glycogenin forms what kind of bond to the reducing end of glucose? |
A beta glycosidic bond |
|
|
On what amino acid does the bond form? |
Tyrosine |
|
|
Per 1 molecule of glycogen, how many glucoses are present? |
60,000 |
|
|
Why is the high cost associated with manufacturing glycogen worth it? |
Because a glycogen molecule can release energy rapidly. This is due to the simultaneous hydrolysis of the alpha (1,6) bonds, usually during the fight-or-flight response. |
|
|
What purpose does cullose serve? |
It serves as a structural polysaccharide |
|
|
What is the structural formula of cellulose? |
(glucose-beta (1,4)-glucose)n |
|
|
What is the structural formula for chitin? |
(N-acetylgalactosamine-beta (1,4)-N-acetylgalactoseamine)n |
|
|
Why does chitin form hard sheets? |
It Hydrogen bonds with itself in anti-parallel chains |
|
|
Glycoproteins are... |
Carbohydrates whose major components are proteins |
|
|
Proteoglycans are... |
Proteins whose major components are carbohydrates |

