![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mostphysiographicfeatures trend in anortherly southerlyDirection like Coast Ranges, Great Valley, Sierra Nevada, except which one?
|
Transverse Range |
|
|
In Santa Barbara if you look at the water you are facing ___. |
South |
|
|
Name the eras in order from oldest to youngest. |
Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic |
|
|
West coast of NorthAmerica was mostly aquiet shallow ocean.Not much happening. Incredibly long period of quiescence on the passive western marginof the North American Continent possibly good fishing while thepassive margin built out. Usually coral, carbonates. Rocking on east North America.
|
Paleozoic |
|
|
Reversal of fortune & tectonic type: Heavy Duty Subduction!Possibly subduction of spreading centers and multiple island arcsystems. Dinosaurs during this time.
|
Mesozoic |
|
|
SAF system (Ridge-Ridge Transform) appears & dominates someaspects of CA fortune. Hypothesis/theory: Transverse Rangesrotate because of oblique subduction & Transform faulting.Mountains build up because of compression caused by bend inSAF. Some Miocene extension. Lateral faulting on SAF, basinsopening/closing,
|
Cenozoic |
|
|
The Transverse Range was made during the Mesozoic & was originally in ___. It got sucked up in a block & rotated __ degrees. |
Mexico; 90 degrees; |
|
|
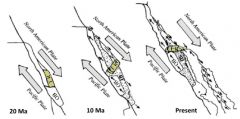
They are out of alignment with the rest of thelarge structures in the state. The theory is that the entire block rotated morethan 90 degrees clockwise to their current position. Trend westerly toeasterly OVER 90degrees of clockwiserotation
|
|
|
|
Rotation of the Transverse Ranges has 3 evidence. |
1. They look out of alignment with most of the other ranges in thestate by about 90 degrees.
2. Paleomagnetic data shows about a 90 degree rotation. 3. Poway Conglomerate is in San Diego & near western end of Transverse range. It’s adistinctive volcaniclastic conglomerate with source area found in Mexico, deposits inSan Diego and probable deposits found in the channel Islands - Santa Cruz andSanta Rosa Islands (Atwater, UCSB) |
|
|
The San Andreas has a __. Big Deal. Pacific plate pushing. It causes compression and squeezes the rocks forming anticlines,synclines, and reverse faults. These form __ and ___. Building up stress & transpression. |
Bend mountains & basins; |
|
|
In California we have right Lateral motion along the San AndreasFault (SAF), a Transform Fault between two spreading-centerridges while the apparent motion of the Pacific Plate is northerly & squeezing the fault from the south. You don’t want to be in the middle of this but Los Angeles is in themiddle of this.
|
KKKKKK |
|
|
A bend in a large fault can create a basin or a mountain range. A ___ bend creates compression and builds mountains. A ___ bend creates a pull apart and creates a basin. Northridge earthquake made mountain move up __ meters.
|
Transpression; Transtension; 2 meters; |
|
|
Anticlines & Synclines from compressional squeeze. Reverse fault & Mega anticline. Why do oil companies like anticlines & synclines? |
This is where oil is at. LA Basin has a lot. |
|
|
Transverse Ranges are all about compression and the mountains are poppingout of the ground really fast - geologically speaking. These mountains aresome of the __ rising mountains in the world. YOU live really close to them.
|
fastest; Ex. San Gabriel, San Antonio, Santa Ynez Mountains; |
|
|
The Channel Islands are part of the Transverse Range. |
True |
|
|
Deposited 12-23 million years ago in Cenozoic time. Exposed throughout coastal California. Source rock for most of California’s petroleum. Composed of deep water sediments with littleto no terrestrial input. Siliceous sediment mostly ___! Also contains porcelanite & dolomite. Takes a lot of time todeposit this much microscopic detritus.
|
Monterey Formation; diatomite; |
|
|
Oil Seep on Santa Barbara area beach. Oil seeps are natural. Oil fields will naturally compress & oil is recharging & locals get mad, but it is natural.
|
ok |
|
|
Los Angeles is ___! SAF zone is moving the area (LA included) ___wardwhile the Pacific Plate is also squeezing it. The surface of the LA basin is heaving up and down. It’s getting squeezed & there is a high likelihood that a __ earthquake is looming. We live in one of the most tectonically ___ andEQ-dangerous area of the world.
|
MOVING; northward; big; active; |
|
|
Summary:
Quiescent Paleozoic. Huge change in Mesozoic from trailing margin to aggressive subduction. Transverse Ranges not in alignment with structures in the rest of California. Transverse Ranges (TR) thought to have been “spun” by Transform Fault dynamics. Late Cenozoic (Miocene) excitement with Transverse Range area being rotated over 90 degreesclockwise current theory. This area saw some extensional tectonics during that time andvolcanism. Amazing stuff! |
Bend in SAF creating compression that is being distributed across the TR areas. Relatively recent (geologically).
Compression can create mountains & valleys & give you Reverse faults/thrust faults. Cenozoic Era marked sedimentary-deposition of biogenic silica in the form of diatomite. Lots of oil can be found in compressional structures in LA basin – and other basins too. Oil helped shape LA society, economy and development. LA (and California) is in a tectonically active part of the world. |

