![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Can we at least tell what is older than what? Refers to what?
|
Relative (age) dating |
|
|
|
How To Imagine “Deep Time”. This is a huge Revolutionary Idea that still creates controversy in some circles. If one second equals one dollar. How much time would it take for you to get a thousand, million, billion, and trillion dollars?*
|
Thousand: 17 minutes (1 inch in 83 feet) Million: 11.6 days (1 inch in 15.8 miles) Billion: 32 years (1 inch in 16,000 miles) Trillion: 32,000 years (1 inch in 16,000,000 miles) |
Geologists don't go as far as a trillion since the earth ain't that old. |
|
|
How do you make a sedimentary rock? |
You take sediments, stack them up and bury them.
|
|
|
|
Where does making sedimentary rock happen? Stuff falls down it and lowers bottom as sediments go there. Creates horizontal layer. Basically Mother Nature has several methods to catch sediment*** |
Basins (like a bowl) |
|
|
|
Know that water flies from high to low. Also, flat areas have __ energy. |
low; |
|
|
|
The younger sediments are at the top and also are more horizontal. The top is flat and the bottom is flecture. We have evidence technology to see how basins are. Horizontal key to sediments. |

|
|
|
|
This cross section has less (if any) vertical exaggeration and is more representative of what subsurface geology can look like. Rocks not in outcrop are determined by projection from the surface plus seismic methods and finally by drilling wells and taking core.
|
What's the point... |
|
|
|
Geologists LOVE to study these modern analogs. Study modern environments and do lab work to understand lithification.
|

|
|
|
|
___ by James Hutton: “The present is the key to the past.” ___ states: “The past may be the key to the future.”*
|
Uniformitarianism*; Corollary |
|
|
|
The process by which sediments become sedimentary rocks.” (Harden) The Process typically involves compaction and loss of fluids.*
|
Lithification* |
|
|
|
What are the four principles of relative dating?* |
Principle of superposition Principle of original horizontality Principle of cross cutting relations Principle of Inclusions |
|
|
|
Principle. The layers at the bottom of a stratigraphic pile are the oldest.
|
Principle of superposition |
|
|
|
Principle. Sediments accumulate in gently sloping or near-horizontal settings.
|
Principle of original horizontality |
|
|
|
Principle. A feature such as a fault that cuts through a layer of rock must be younger than that layer of rock being cut. |
Principle of cross cutting relations |
|
|
|
Principle. A rock or sediment containing fragments of other rocks must be younger than the rock it contains. |
Principle of Inclusions |
The one inside is older |
|
|
Older is usually on the bottom. One exception would be ___ coming up from below.
|
Volcanic intrusive; |
|
|
|
____ is WHACK because grab sandstone from top and somehow become younger than the sandstone it has as an inclusion now. Don't worry about knowing this just know it's WHACK. |
plutonic granite |
|
|
|
Gaps in the geologic record. It is a surface that represents a gap in the geologic record that may indicate episodes of crustal deformation, erosion, and sea level variations. They are features of stratified rocks and are therefore usually found in sediments (but may also occur in stratified volcanics). They are surfaces representing substantial breaks in the geologic record.THEY ARE A BIG DEAL*****
|
Unconformity (Unconformities) |
How do you recognize that something is not there? Or, how do you recognize something that is not there?
|
|
|
Name the 3 types of Unconformities. |
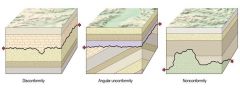
Angular Unconformity Nonconformity Disconformity |
|
|
|
Unconformity where the layers below have a different orientation than the layers above
|
Angular Unconformity |
Long period of time has gone by between the layers. |
|
|
Unconformity where sedimentary rocks overlie igneous or metamorphic rocks. |
Noncomformity |
|
|
|
Unconformity where beds above and below surface are parallel, but part of the sequence is missing. Often times tough to identify but paleontology helps. |
Disconformity |
|
|
|
Although some species have persisted through long stretches of geologic time without much change, others made only brief appearances on Earth. The presence of these time-specific, characteristic __ is useful. Helps identify rocks formed during the same restricted time interval, even if the rocks are found in widely separated areas.*
|
index fossils |
Simply put, used to identify distinctive layers. (can find them all around the world) |
|
|
1769-1839, Surveyor/geologistGreat Britain recognized distinctive sed. rock layers.
- Identified the fossil assemblage within specific layers - Realized particular fossil species found only in a ___ interval* •once a particular fossil disappears -it is never found higher in the sequence (unless reworked in a sedimentary cycle)* •extinction is forever –think again about why this is important to correlation.* -Same observation recorded around the world. Codified as ___. Can determine ___* of strata by looking at fossils |
William "strata" Smith; limited; Fossil Succession or The Principle of Faunal Succession; relative ages |
Flora is plants and fauna is animals |
|
|
By studying the succession of fossils, Paleontologists have been able to lay out the framework of life’s evolution.
Archean eon: __ appeared. Late Proterozoic eon: ___ appeared. Precambrian/Cambrian boundary: _____? Ordovician Period: ____ Silurian Period: ____ (all life before was marine (deep or shallow)). Devonian: |
simple bacteria;*
complex invertebrates;* invertebrates with SHELLS;* first vertebrates, fish;* First multicellular life ON LAND, land plants spread;* amphibians* |
|
|
|
Pennsylvanian: ____
Triassic: ___ on land & extinct by the ____. sudden and massive. Mesozoic is called the ____. Cenozoic is called ____. (though they appeared in the Triassic (part of the Mesozoic) they diversified in the Cenozoic) |
First reptiles;* dinosaurs;* Cretaceous;* Age of the Dinosaurs; Age of Mammals |
|
|
|
Name three microfossils |
Diatoms (oil groups love these) Radiolaria(ns) Foraminifera (good index fossil) |
|

