![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
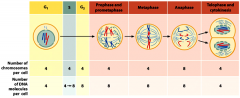
The eukaryotic cell division cycle consists of what phases?
|
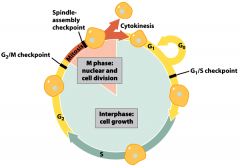
G1 (gap 1): cell growth
S-phase (synthesis): DNA replication G2 (gap 2): cell growth M-phase: nuclear and cell division (mitosis + cytokinesis) Cytokinesis: the cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, bringing about the separation into two daughter cells. Interphase: G1 + S + G2 + the cell may exit the division cycle at G1 and go into G0 to become a non-dividing cell. |
|
|
What is interphase?
|
Interphase (cell growth): G1 + S + G2
+ the cell may exit the division cycle at G1 and go into G0 to become a non-dividing cell. |
|
|
When is DNA single stranded and double stranded during the eurkaryotic cell division cycle?
|
+ at the end of mitosis and during G1: each chromosome consists of a single DNA molecule
+ after S-phase and during G2: each chromosome consist of two DNA molecules (two sister chromatids) |
|
|
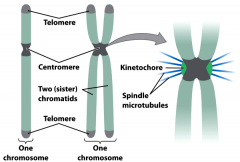
What are chromosomes consisting of two DNA molecules called?
|
Sister chromatids
|
|
|
What is a centromere:
|
Centromere: the region of the chromosome in which sister chromatids are joined (also present before DNA replication).
|
|
|
Telomeres:
|
Telomeres: stable ends of linear chromosomes
|
|
|
What is chromatin and what does it consist of?
|
Chromatin: the material of which the chromosomes of organisms other than bacteria (i.e., eukaryotes) are composed. It consists of protein, RNA, and DNA.
+fibers of decondensed DNA chromosomes +occurs during nondivisional phases of the cell cycle |
|
|
What happens to chromatin prior to cell division?
|
Prior to cell division, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes due to the tightening of interactions between DNA and chromatin proteins (histones)
|
|
|
What are chromatin proteins called?
|
Chromatin proteins are called histones.
|
|
|
What is a chromosome?
|
Chromosome
+before DNA replication: a single molecule of DNA +following DNA replication in preparation for cell division - chromosomes consist of two sister chromatids, which contain identical DNA sequences |
|
|
Define:
metacentric submetacentric acrocentric telocentric p arm q arm |
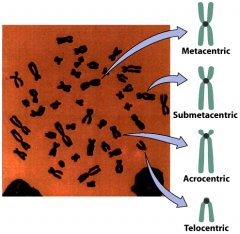
Classification of chromosomes based on centromere location
metacentric: middle submetacentric: between middle and end acrocentric: close to end telocentric: at end p arm ("petite"): short arm of the chromosome q arm: long arm, always shown below the centromere |
|
|
Define:
Haploid Diploid |
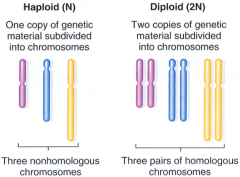
Haploid (N): One copy of genetic material subdivided into chromosomes. (no pairs)
Diploid (2N): Two copies of genetic material subdivided into chromosomes. (pairs) |
|
|
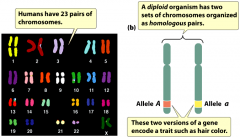
+How many homologous chromosomes do humans have?
+ What are alleles? |
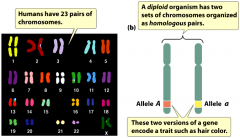
+23 pairs of homologous chromosomes paired together.
+Alleles: alternative forms of a gene found at the same position of homologous chromosomes. The two alleles of diploid organisms encode for a trait, such hair colour. |
|
|
What makes 2 chromosomes homologous?
|
+Chromosomes with identical length and centromere location
+They contain the same genes but not necessarily identical DNA sequences (some of their genes may be allelic) |
|
|
During which part of cell division is DNA the most condensed?
|
Metaphase
|
|
|
What is a human karyotype?
|
Shows all 2 homologous pairs of autosomal (non sex-determining) chromosomes plus the pair of sex chromosomes.
|
|
|
Define:
diploid haploid polyploid aneuploid |
diploid: 2N
haploid: N polyploid: 3n, 4n, 5n, etc. aneuploid: none of the above (having particular genes or chromosomal regions present in extra or fewer copies than in the normal type.) |
|
|
Define:
DNA replication Mitosis Cytokinesis |
DNA replication: duplication of the chromosomes (result: sister chromatids)
Mitosis: division of the nucleus Cytokinesis: division of the cytoplasm (the rest of the cell) |
|
|
What is the difference between mitosis and cytokinesis?
|
Mitosis= division of nucleus
cytokinesis=division of cytoplasm (the rest of the cell) |
|
|
What happens during mitosis?
|
During mitosis, spindle microtubules are attached to the centromeres, and the sister chromatids are segregated.
|
|
|
What are the phases of Mitosis?
|
Prophase
Prometaphase/ metaphase Anaphase Telophase |
|
|
What happens during prophase?
|
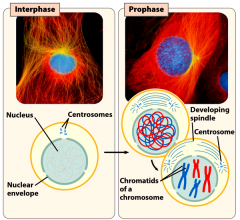
Prophase: the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes (with the help of histone proteins)
|
|
|
What happens during prometaphase/ metaphase?
|
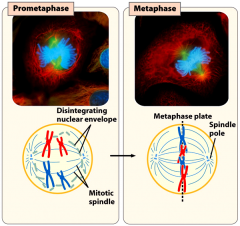
The nuclear envelope disintegrates, the mitotic spindle (microtubules) attach to the centromeres of the chromatids, and the chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate.
|
|
|
What happens during anaphase?
|
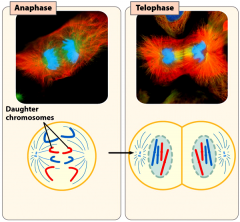
the chromatids are pulled apart by the mitotic spindle.
|
|
|
telophase:
|
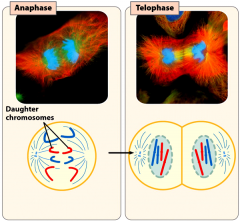
the chromotids are segregated and their DNA decondenses. The chromatids become the chromosomes of the daughter cells.
|
|
|
What is the outcome of mitosis in diploid cells?
|
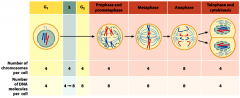
-Outcome: two diploid nuclei.
-Cytokinesis follows (in most cases). -The nuclear envelope may or may not dissolve during prophase (mitosis may be open or closed). |
|
|
What might halt the progression through the cell division cycle?
|
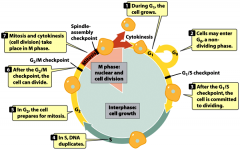
-The progression through the cell division cycle may be halted
at checkpoints due to DNA damage, incomplete DNA replication, insufficient cell size, or incomplete mitotic spindle formation. -the cycle is resumed after problems are fixed -the cell may exit to G0 in response to outside signals -if cell damage is too extensive, the cell may be induced to die -if cell division controls are defective: uncontrolled cell proliferation (tumors, cancer) |
|
|
What is meiosis?
|
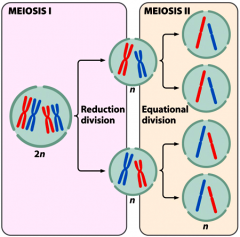
+Meiosis is a special type of cell division cycle that occurs during the generation of gametes (sperm and egg) or spores.
+two rounds of cell divisions +outcome: four haploid (1n) cells |
|
|
Define these substages of meiotic prophase 1:
Leptotene Zygotene Pachytene Diplotene Diakinesis |
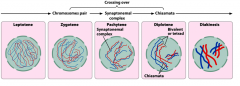
Leptotene: DNA begins to partially condense with the help of histone proteins.
Zygotene: homologous chromosomes pair to form tetrads (or bivalents). The synaptonemal complex begins to form. Pachytene: condensation continues and the sister chromatids of the chromosome are visible. DNA exchange occurs (crossing over). Diplotene: homologous chromosomes begin to pull apart. The chiasmata become visible: regions in which DNA exchange occurred. Diakinesis: the chromosomes pull further apart. Further condensation occurs. |

