![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an electron carrier? |
A molecule that is capable of accepting one or two electrons from one molecule and donating them to another in the process of electron transport. As the electrons are transferred from one electron to another, their energy level decreases and energy is released. |
|
|
What are NAD+ and FAD+ and what do they act as? |
Low energy oxidized coenzyme that act as electron acceptors. |
|
|
What is to oxidize? |
To combine or become combined chemically with oxygen. |
|
|
What happens when electrons are added to NAD+ and FAD+? |
They become reduced to NADH and FADH² |
|
|
What is NADH? |
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
|
|
What is FADH2, when is it created and where is it utilized? |
Flavin adenine dinucleotide is a reduced coenzyme and an energy carrying molecule created during the Krebs cycle and is utilized during the last part of respiration, the electron transport chain. |
|
|
What is NADH a reduced form of? |
NAD |
|
|
What is ATP and what is it composed of? |
Phosphorylated nucleotide composed of adenosine and three Phosphate groups |
|
|
What does ATP supply and how does it do this? |
Supplies energy for biological processes by undergoing enzymatic hydrolysis |
|
|
What is ADP and how is it converted to ATP? |
Adenosine triphosphate, composed of adenosine and two Phosphate groups that is converted to ATP for the storage of energy during cell metabolism when a Phosphate group is added. |
|
|
What is Substrate-level Phosphorylation and where does it take place? |
A metabolic reaction where ATP forms directly in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction when a Phosphate group is taken from an compound added to ADP. Takes place in the mitochondria during the Krebs cycle. |
|
|
How does oxidative phosphorylation work? |
The process of forming ATP via the transfer of electrons. ATP forms indirectly through a series of enzyme-related redox reactions involving oxygen as the final electron acceptor. ATP is generated from the oxidation of NADH and FADH2 and the summer sequent transfer of electrons and pumping of protons. |
|
|
What does oxidative phosphorylation generate and what is it used for? |
Generates an electrochemical gradient which is required to power the ATP synthase |
|
|
Where does oxidative phosphorylation take place? |
The mitochondria |
|
|
Where do 26 of the total 30 ATP molecules generated from a single glucose molecule come from? |
oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
What is the final step of cellular respiration? |
oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction |
A type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two spices, and chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of a molecule, atom, or ion changes by gaining or losing an electron. Oxidation: gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen Reduction: the loss of oxygen or gain of hydrogen |
|
|
Carbon Fixtion |
Fixing carbon into one place; taking inorganic carbon (usually CO2) and tacking it to an organic molecule (usually a carbohydrate) The process by which photosynthesis organisms such as plants turn inorganic carbon (usually carbon dioxide) into organic compounds (usually carbohydrates) The conversion of carbon dioxide into organic compounds during photosynthesis |
|
|
NADH dehydrogenase |
The weakest attractor of electrons The first complex in the electron transfer chain of mitochondria and catalyzes the transfer of electron from NADH to coenzyme Q |
|
|
ATP synthase |
An enzyme that creates ATP from ADP and inorganic Phosphate, needs energy
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of ATP from the phosphorylation of ADP with inorganic Phosphate (Pi) using a form of energy such as the energy from a protein gradient
An enzyme that can synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic Phosphate by utilizing some form of energy |
|
|
Cellular Respiration Full Cycle Chart |
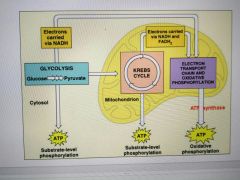
|
|
|
Aerobic Respiration Stages |
1. Glycolysis: 10-step process in the cytoplasm 1. Pyruvate Oxidation: 1-step process in the mitochondrial matrix 3. Krebs Cycle: 8-step cyclical process in the mitochondrial matrix 4. Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis: multistep process in the inner mitochondrial membrane |
|
|
Glycolysis Steps |
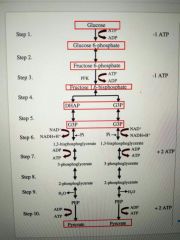
2 ATP are used in steps 1 and 3 to prepare glucose for splitting F, 1, 6-BP splits into DHAP and G3P DHAP converts to G3P 2 NADH are formed in step 6 2 ATP are formed by substrate-level phosphorylation in both steps 7 and 10 2 pyruvates are produced in step 10 |
|
|
Glycolysis Energy Yield and Products |
4 ATP produced - 2 ATP used =2 net ATP 2 NADH 2 pyruvates Further processing in aerobic cellular respiration (if oxygen is available) |
|
|
Mitochondria Diagram |
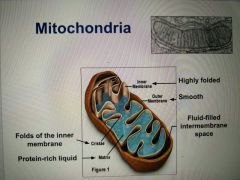
|
|
|
Pyruvate Oxidation (if oxygen is present) |
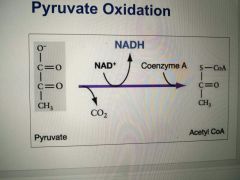
1. CO2 is removed 2. NADH+ reduced to NADH and the 2-carbon compound becomes acetic acid 3. Coenzyme A (CoA) attaches to acetic acid to form acetyl-CoA |
|
|
Pyruvate Oxidation Energy Yield and Products |
2 NADH 2 acetyl-CoA 2 CO2 (released as waste) |
|
|
Krebs Cycle Steps |
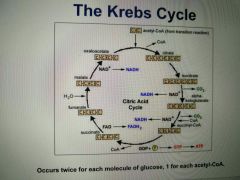
1. In step 1, acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate 2. In step 2, citrate is rearranged to isocitrate 3. NADH+ is reduced to NADH in steps 3, 4, and 8 4. FAD is reduced to FADH2 in step 6 5. ATP is formed in step 5 by substrate-level phosphorylation. The Phosphate group from succinyl-CoA is transferred to GDP, forming GTP, which then forms ATP 6. In step 8, oxaloacetate is formed from malate, which is used as a reactant in step 1 7. CO2 is released in steps 3 and 4 |
|
|
Krebs Cycle Energy Yield and Products |
2 ATP 6 NADH 2 FADH2 4 CO2 (released as waste) NADH and FADH2 carry electrons to the electron transport chain for further production of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
Electron Transport Chain (ETC) |
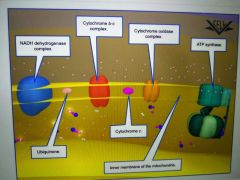
A series of electron acceptors (proteins) are embedded in the cristae |
|
|
How are the proteins in the ETC arranged and what starts and ends the chain? |
In order of increasing electronegativity. The weakest attractor of electrons (NADH dehydrogenase) is at the start of the chain and the strongest (cytochrome oxidase) is at the end. |
|
|
How do proteins pass electrons in the ETC? |
Pass electrons from NADH and FADH2 to one another through a series of redox reactions. ETC protein complexes are alternately reduced and oxidized as they accept and donate electrons. As the electrons pass from one molecule to the next, it occupies a more stable position. |
|
|
What is the free energy released from the ETC used for and what does it create? |
Used to pump protons (H+) to the intermembrane space. 3 for every NADH and 2 for every FADH2 Creates an electrochemical gradient, creating potential difference (voltage) similar to a battery |
|
|
Where do protons enter the matrix in the ETC? |
Through proton channels associated with ATP synthase |
|
|
How much free energy is released for every H+ that passes through the ETC? |
Enough free energy is release do create 1 ATP from phosphorylation of ADP |
|
|
Why must the conditions of the ETC be aerobic? |
Conditions must be aerobic because oxygen acts as the final electron and H+ acceptor (water if formed as a byproduct) |
|
|
ETC Diagram |
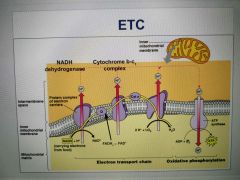
|
|
|
ATP Yield from Aerobic Respiration |

|
|
|
How is aerobic respiration regulated? |
Regulated by feedback inhibition and product activation loops. |
|
|
Phosphofructokinase (PFK) |
An allosteric enzyme that catalyzes the third reaction in glycolysis and is inhibited by ATP and stimulated by ADP. |
|
|
What happens if citrate accumulates? |
If citrate accumulates, some will enter the cytoplasm and inhibit PFK to slow down glycolysis. |
|
|
What happens when citrate is used up? |
As citrate is used up, its concentration will decrease and the rate of glycolysis will increase. |
|
|
What does a high concentration of NADH indicate? |
That the ETCs are full of electrons and ATP production is high. |
|
|
What does NADH allosterically inhibit? |
NADH allosterically inhibits an enzyme that reduces the amount of acetyl-CoA that is shuttled to the Krebs cycle, reducing the amount of NADH produced. |
|
|
Allosteric |
Of or relating to the binding of a molecule to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, resulting in modulation of the enzyme's activity as a result of a change in its shape. |

