![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Addition Reaction |
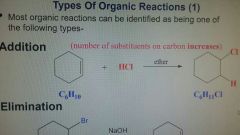
Number of substituents on carbon increase. |
|
|
Elimination Reaction |
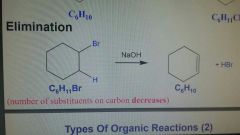
Number of substituents on carbon decreases |
|
|
Substitution reaction |
Number of substituents remain the same. |
|
|
Breaking bonds symmetrically |
Use fish hook arrows that transfer 1 electron. Associated with radical reactions. Homolytic bond breakage. |
|
|
Non-symmetrical bond break |
Bond breaks towards more electronegative atom. Full head arrow, moves electron pairs, associated with polar reactions. |
|
|
Nucleophile |
Electron rich atoms or molecules. Lewis base. Have an electron pair to share. |
|
|
Epectrophile |
Electron deficient atoms or molecules. Lewis Acid. Can accept a pair of electrons. |
|
|
Spontaneous reaction |
Gibbs free energy is negative - Enthalpy (♢H°) is negative - Entropy (♢S°) is positive |
|
|
Non spontaneous reaction |
Gibbs free energy is positive - Enthalpy (♢H°) is positive - Entropy (♢S°) is negative |
|
|
Reactants favoured reaction |
- Keq < 1 - ♢H° > 0 - ♢G° > 0 - ♢S° < 0 |
|
|
Products favoured reactions |
- Keq > 1 - ♢H° < 0 - ♢G° < 0 - ♢S° > 0 |
|
|
Rate determining step |
Largest energy step. Trough to trough. |
|
|
Catalyst |
Lowers activation energy. Does not change energy of start or endpoint. |
|
|
Enzymes |
Biological proteins, found in bodies and act as catalysts. |
|
|
Exergonic |
A release of energy. When spontaneous. G<0 |
|
|
Endergonic |
When energy is absorbed. When non-spontaneous. G>0 |

