![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of epithelium lines the skin of the penis and the tip of the urethra?
|
Squamous epithelium
|
|
|
What type of epithelium lines the posterior 1/3 of the urethra?
|
Transitional epithelium
|
|
|
Where do Primordial Germ Cells develop in?
|
Yolk Sac
|
|
|
From the Yolk Sac, the PGC's migrate into the __1__ that form on the posterior wall of the __2__. Genital ridges interact with the __3__ and __4__ ducts, which give rise to internal genital organs
|
1. Genital ridges
2. Celomic cavity 3. Mullerian 4. Wolffian |
|
|
The male genital organs develop from this duct
|
Wolffian (Mesonephric)
*Mullerian ducts involute |
|
|
Female organs develop from what duct?
|
Mullerian (Paramesonephric)
*Wolffian ducts invole |
|
|
During fetal life, through what canal do the testes descend to reach the scrotum?
|
Inguinal canal
|
|
|
The transabdominal phase of descent, when testes descend to the pelvic brim, is dependent on what factor?
|
Mullerian Inhibitory factor
|
|
|
The inguinoscrotal phase of testes descent is dependent on what factor?
|
Androgens
- testosterone - DHT - Androstenedione |
|
|
The penis develops from the __1__, the same structure that gives rise to the __2__ in women
|
1. Genital tubercle
2. Clitoris |
|
|
The __1__, the primordia of the labia in females, fuse in the midline in the male fetus thus forming the __2__
|
1. Labiaoscrotal folds
2. Scrotum |
|
|
The penile urethra forms from the _______ that closes on the lower side
|
Urogenital sinus
|
|
|
What 2 things do the tesis consist of and what does each contain?
|
1. Seminiferous tubules = Spermatogenic epithelium + Sertoli cells
2. Interstitial tissue = Leydig cells |
|
|
anomaly in which the urethral meatus opens on the ventral (inferior/bottom) surface of the penis
|
Hypospadia
|
|
|
Anomaly in which the urethral meatus opens on the dorsal (superior/top) surface of the penis
|
Epispadia
|
|
|
What is Hypospadia due to a failure of?
|
The urethral folds to close
|
|
|
What is Epispadia due to?
|
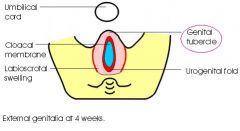
Faulty positioning of the Genital Tubercle
|
|
|
What is Epispadia often associated with?
|
Extrophy of the Bladder
|
|
|
Which is more common: Hypospadia or Epispadia?
|
Hypospadia
|
|
|
What is the most common abnormality of the male genital tract?
|
Cryptorchidism (1 in 200)
|
|
|
When is Cryptorchidism more commonly found?
|
Prematurely born boys
|
|
|
Complete or incomplete descent of the testis into the scrotal sac
|
Cryptorchidism
|
|
|
Surgical repositioning of the testis into the scrotum = ?
|
Orchidopexy
|
|
|
What is the most common site for Cryptorchid testis?
|
Inguinal canal
|
|
|
What are the 2 major complications of Cryptorchidism?
|
1. Germ cell tumors = Seminoma
2. Infertility = testicular atrophy and seminal epithelium degeneration |
|
|
What is the cause of Infertility in Cryptorchidism?
|
High body temperature in undescended testes decreases Spermatogenesis
|
|
|
Abnormally tight foreskin that is difficult or impossible to retract over the glans of the penis
|
Phimosis
|
|
|
What is the most common site on the penis for Hypospadia to occur and why?
|
Near the GLANS b/c it zips up proximally to distally
|
|
|
Why might it be a good idea to remove the tesis with Cryptorchidism?
|
B/c there is a 5-fold increase risk of Germ Cell Cancer (Seminoma)
|
|
|
During fetal life, what is the major source of Anti-Mullerian hormone?
|
Sertoli cells
|
|
|
What cells in the testes produce Androgens?
|
Leydig cells
|
|
|
What cell produces Anti-meiotic factor and what is its function?
|
Sertoli cells
prevents Spermatogenesis until puberty |
|
|
What are the 2 groups of Pretesticular infertility?
|
Hypothalamus
Pituitary |
|
|
Kallmann's Syndrome is a maldevelopment of these 2 things
What do these maldevelopments cause? |

Olfactory bulbs = anosmia = lack of smell
GnRH producing cells = released from hypothalamus and is responsible for the release of FSH and LH from Anterior Pituitary - LH -> Leydig -> Androgens -FSH -> Sertoli -> Sperm production |
|
|
What is released from Sertoli cells that decreases FSH release?
|
Inhibin
|
|
|
What are 3 Congenital Syndrome that could cause Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism?
|
1. Kallmann
2. Prader-willi 3. Frohlich syndrome |
|
|
What 2 tumors could cause Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism resulting in infertility?
|
Craniopharyngioma
Pituitary adenoma |
|
|
What 2 inflammatory conditions could cause Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism resulting in fertility?
|
Sarcoidosis
Tuberculosis |
|
|
Syndrom with Androgen deficiency resulting in Testicular Infertility
|
Klinefelter Syndrome
|
|
|
What does Androgen receptor failure result in?
|
Testicular feminization and infertility
|
|
|
What 4 things could cause Spermatogenic failure leading to infertility?
|
1. Germ cell aplasia
2. Maturation arrest 3. Orchitis 4. Chemotherapy |
|
|
Describe "Del Castillo Syndrome"
|
Seminiferous tubule with no sperm and no spermatogonia = "Sertoli-only syndrome"
|
|
|
What are 3 causes of Post-testicular Infertility?
|
1. Cystic fibrosis
2. Epididymitis 3. Vasectomy |
|
|
Why are most males with Cystic Fibrosis infertile?
|
they are missing the Vas Deferens
|
|
|
Accumulation of fluid in the scrotum = ?
|
Hydrocele
|
|
|
What is the fluid in Hydrocele usually contained within?
|
between the 2 layers of Tunica vaginalis
|
|
|
How are Hydrocele and Testicular tumors differentiated?
|
Transillumination = hydrocele
|
|
|
What is a Scrotal Hernia?
|
loops of the intestine slide into the scrotum
|
|
|
Inflammation of the Testes and Epididymus = ?
|
Epididymo-orchitis
|
|
|
What are some common bacteria that cause Epididymo-orchitis?
|
1. N.gonorrhoeae
2. M. tuberculosis 3. M. leprae 4. T. pallidum = Syphillis |
|
|
How does Syphilis usually manifest itself?
|
Painless chancre
|
|
|
What virus used to commonly cause Orchitis?
|
Mumps
|
|
|
How does Epididymitis present clinically?
|
Scrotal pain with radiation into the spermatic cord
|
|
|
Inflammation of the glans penis = ?
|
Balanitis
|
|
|
Inflammation of the glans penis and foreskin
|
Balanoposthitis
|
|
|
Subcutaneous fibrosis of the dorsum of the penis that occurs in older men
- results in lateral curvature |
Peyronie disease
|
|
|
Persistent and painful erection sometimes associated with Venous Thrombosis of the Corpora Cavernosa
|
Priapism
|
|
|
Purulent urethral discharge examined under the microscope as paired cocci in the cytoplasm of neutrophils
|
N. gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
What gender is Cystitis more common in and why?
|
Women b/c their urethra's are shorter = bladder is more easily invaded by bacteria
|
|
|
Is Cystitis more commonly due to an Ascending or Descending route of infection?
|
Ascending
|
|
|
What are 4 predisposing factors for getting Cystitis
|
1. Shorter urethra in women
2. Prostatic disease in elderly men 3. Instrumentation (catheter) / drugs 4. Urinary stones |
|
|
What drug sometimes causes Pseudomembranous Cystitis?
|
Cyclophosphamide
|
|
|
In Egypt, what is often the cause of Cystitis?
|
Schistosoma Haematobium
|
|
|
Chronic inflammation of the urinary bladder of unknown etiology
|
Interstitial cystitis
|
|
|
Who is most often affected by Interstitial Cystitis?
|
Women ages 30-70
|
|
|
What are the 2 forms of Interstitial Cystitis on cytoscopy and at what age do they peak?
|
1. Non-ulcerous = 40 years of age
2. Hunner ulcers = 60 years of age |
|
|
What is the most common cause of left-sided Scrotal enlargement in adults and why?
|
Varicocele
-b/c the left spermatic vein drains into the left renal vein |
|
|
Hypospadia
|
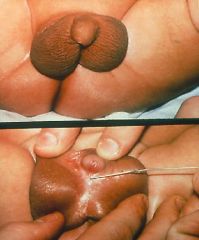
What is this?
|
|
|
Epispadia + Extrophy of the Bladder
|
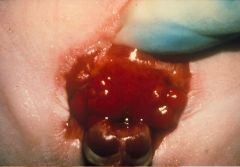
What is this?
|
|
|
Cryptorchidism
|
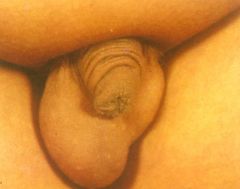
What is this?
|
|
|
Cryptorchidism
-testes small, atrophic, and fibrotic |
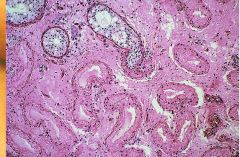
What is the cause of this?
|
|
|
Germ cells with no sperm = infertility
Prader-Willi Syndrome |
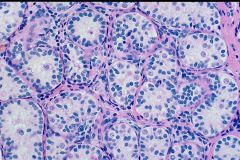
What is this?
What Syndrome? |
|
|
Seminiferous tubule with no sperm = no spermatogonia
"Sertoli-only Syndrome" = Del Castillo Syndrome |
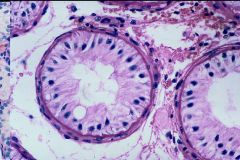
Describe what you see
What syndrome? |
|
|
Seminiferous tubule with Spermatogenic arrest at the Spermatogoium level
|
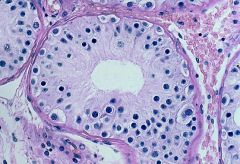
What do you see here?
|
|
|
Spermatogenic arrest at the Round Spermatid level
|
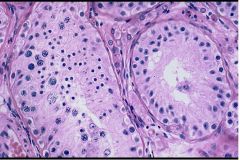
What do you see here?
|
|
|
Hydrocele = fluid within the Tunica Albuginea
|
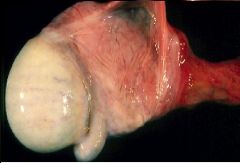
What is shown here?
|
|
|
Epididymal cysts
|
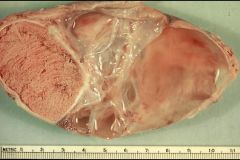
What are these?
|
|
|
Epididymitis
|
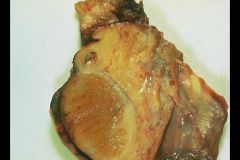
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Cystitis with hemorrhaging
-hemorrhaging is one of the most common symptoms of cystitis |
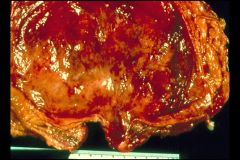
What is shown here?
|
|
|
Cystitis -> indwelling catheter
|
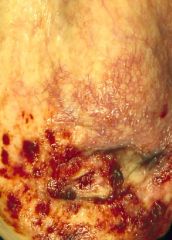
What is the most likely cause of this lesion?
|
|
|
Bladder with infiltration of plasma cells and lymphocytes
-transitional epithelium |
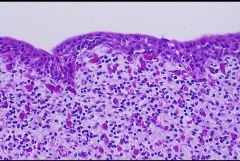
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Cystitis caused by Schistosoma hematobium
-person is most likely from Egypt |
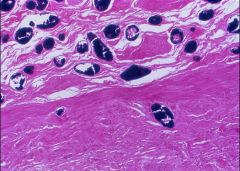
What is this?
|
|
|
Hunner ulcer
60 years old Interstitial Cystitis |
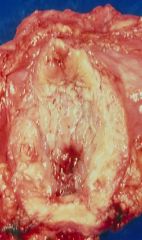
What is this lesion?
What age group does it usually present in? What disease? |

