![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
342 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the mouth? |
Oral or buccal cavity |
|
|
What is the function of the mouth? |
Site of mechanical & chemical digestion |
|
|
What is the hard palate? |
Bone partition between nasal & oral cavities |
|
|
What is the function of the soft palate? |
Closes off nasopharynx to oropharynx during swallowing |
|
|
What is the function of the uvula? |
Closes off nasopharynx during swallowing |
|
|
What are the functions of the tonsils? |
Immune response against foreign inhaled & ingested substances |
|
|
What are the various tonsil types & how many of each are there? |
--Palatine (2) - both sides of oral fauces --Lingual (2) - inferior to tongue --Pharyngeal (1) - just behind internal nares |
|
|
What produces lingual lipase? |
Tongue |
|
|
What is the tongue? |
Skeletal muscle accessory organ w/ mucous membrane attached to hyoid bone |
|
|
What digestive enzyme is produced by the tongue? |
Lingual lipase |
|
|
What are the teeth? |
Accessory organ in sockets of alveolar processes of mandible & maxillae |
|
|
What are alveoli (of teeth)? |
Alveolar processes of mandible & maxillae |
|
|
What are the gingivae (gums)? |
Protrusions of mucous membrane that extend slightly into each socket |
|
|
What tissue does the periodontal membrane consist of? |
Dense fibrous CT |
|
|
What is the function of the periodontal membrane? |
Ligament that anchors teeth to socket walls |
|
|
What is the crown (of the tooth)? |
Visible portion of tooth (above gums) |
|
|
What is the root (of the tooth)? |
Portion of tooth embedded in socket |
|
|
How many roots does each tooth have? |
1 to 3 |
|
|
What forms the majority of a tooth's structure? |
Dentin |
|
|
What does dentin consist of? |
Calcified CT (70% of dry weight is Ca2+ salts) |
|
|
What is the function of dentin? |
Gives tooth base shape & rigidity |
|
|
What is the hardest surface in the body? |
Tooth enamel |
|
|
What is the function of tooth enamel? |
--Protects tooth from wear & tear of chewing |
|
|
What is the function of cementum? |
Bone-like structure that attaches root to periodontal ligament |
|
|
What is pulp? |
CT containing: --Blood vessels --Nerves --Lymphatic vessels |
|
|
What is the root canal? |
Extension of pulp cavity where root of tooth runs through |
|
|
What is the apical foramen? |
Opening @ base of root canal containing: --Blood vessels --Nerves --Lymphatic vessels |
|
|
What is the neck (of teeth)? |
Junction b/w crown & root (near gum line) |
|
|
What is the dental formula? |
3 molars 2 premolars 1 canine 2 incisors |
|
|
What are the incisors? |
2 teeth closest to midline |
|
|
What is the function of the incisors? |
Used for cutting into food |
|
|
What are the canines? |
Tooth immediately lateral to incisors on either side (R & L) |
|
|
What is the function of the canines? |
Used to tear & shred food |
|
|
What are the premolars? |
2 teeth lateral & posterior to canine on either side (R & L) |
|
|
What is the function of the premolars? |
Crush & grind food |
|
|
How many roots do the premolars have? |
2 - 3 |
|
|
What are the molars? |
3 teeth posterior to premolars |
|
|
What is the function of the molars? |
Crush & grind food |
|
|
What are the groups of salivary glands (& ducts)? |
--Parotid --Submandibular --Sublingual |
|
|
What is the function of salivary glands (& ducts)? |
Produce watery saliva to aid in mechanical digestion & amylase |
|
|
What are the main products of the parotid salivary glands? |
Amylase |
|
|
Where are the parotid salivary glands? |
Inferior & anterior to ears |
|
|
What are the main products of the submandibular salivary glands? |
Amylase & mucus |
|
|
Where are the submandibular salivary glands located? |
Floor of mouth |
|
|
What is produced by the sublingual salivary glands? |
Mostly mucus |
|
|
Where are the sublingual salivary glands located? |
Beneath the tongue, superior to submandibular glands |
|
|
What is the function of the pharynx? |
Passageway for air & food |
|
|
What is the fauces? |
Opening connecting oral cavity & oropharynx |
|
|
What is the oropharynx? |
Common passageway for air/food |
|
|
What is the laryngopharynx? |
Passageway to propel food toward esophagus |
|
|
What is the nasopharynx? |
Passageway for air |
|
|
What is the esophagus? |
Collapsible muscular tube connecting pharynx to stomach |
|
|
What is the function of the esophagus? |
Propel food (bolus) towards stomach via peristalsis |
|
|
What is the function of the stomach? |
--Mixes & holds food --Converts semi-solid bolus to liquid |
|
|
What is the function of the longitudinal, circular, & oblique muscles (of stomach/esophagus)? |
Peristalsis |
|
|
What muscle is present in the muscular layers of the stomach that is not present in the esophagus? |
Oblique muscles |
|
|
What is the cardiac (AKA - lower esophageal) sphincter? |
Circular band of smooth muscle connecting esophagus to stomach |
|
|
What is the function of the cardiac (AKA - lower esophageal) sphincter? |
Keep gastric juices from entering esophagus |
|
|
What is the pyloric sphincter? |
Circular band of smooth muscle connecting stomach to duodenum of sm. intestine |
|
|
What is the function of the pyloric sphincter? |
Regulate the flow of chyme from stomach to duodenum of sm. intestine |
|
|
What is the greater curvature (of the stomach)? |
Convex, lateral border |
|
|
What is the lesser curvature (of the stomach)? |
Concave, medial border |
|
|
What is the body (of the stomach)? |
Lg., central portion of the stomach |
|
|
What is the fundus (of the stomach)? |
Rounded portion of stomach superior & to L of cardia |
|
|
What is the pyloric region (of stomach)? |
Inferior part of stomach connecting to duodenum |
|
|
What is the pyloric atrium? |
Connects body of stomach |
|
|
What is the pyloric canal? |
Leads to pylorus |
|
|
What is the pylorus? |
Leads to duodenum |
|
|
What are the rugae (of stomach)? |
Folds in mucosa of stomach (when stomach is empty) |
|
|
What are the plicae circulares? |
Mucosal & submucosal folds that go around the small intestine |
|
|
What is the function of the plicae circulares? |
Increase surface area |
|
|
What are villi (of small intestine)? |
Projections off of plicae |
|
|
What is the 1st part of the small intestine? |
Duodenum |
|
|
What is the function of the duodenum? |
Site of absorption |
|
|
What is the duodenal papilla? |
Opening of the common bile duct into the duodenum |
|
|
What is the function of the duodenal papilla? |
Primary mechanism for the secretion of bile |
|
|
What is another name for the duodenal papilla? |
Papilla of Vater |
|
|
What is the hepatopancreatic duct? |
The cavity behind the duodenal papilla |
|
|
What is another name for the hepatopancreatic duct? |
Ampulla of Vater |
|
|
What is the function of the Sphincter of Oddi? |
Regulate flow of pancreatic juice & bile into duodenum |
|
|
What is the jejunum? |
Second part of sm. intestine that extends into illium |
|
|
What is the ileum? |
Third & last segment of sm. intestine |
|
|
What is the ileocecal valve? |
Smooth muscle sphincter that opens from sm. intestine into lg. intestine |
|
|
What is the function of the pancreas? |
Secretes pancreatic juice, bicarbonate, and hormones (i.e., insulin & glucagon) |
|
|
What are the sections of the pancreas? |
--Head --Neck --Body --Tail |
|
|
What is the pancreatic head? |
Expanded portion of pancreas near curve of duodenum |
|
|
What is the pancreatic tail? |
Tapering portion of pancreas near spleen |
|
|
What is the pancreatic body? |
Majority of the pancreas |
|
|
What is the pancreatic neck? |
Portion of pancreas between the pancreatic neck & body |
|
|
What is the function of the principal pancreatic duct? |
Drains into ampulla of Vater & joins the common bile duct |
|
|
What is the function of the accessory pancreatic duct? |
Leads to pancreas & empties into duodenum |
|
|
Which is the larger of the pancreatic ducts? |
Principal pancreatic duct |
|
|
What divides the R & L lobes of the liver? |
Falciform ligament |
|
|
What is the function of the falciform ligament? |
Connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall |
|
|
Where is the ligamentum teres located? |
Extends from liver to umbilicus |
|
|
What feature is the remnant of the umbilical vein of the fetus? |
Ligamentum teres |
|
|
What is the function of the hepatic artery? |
Supply O2 rich blood to liver |
|
|
What is the function of the hepatic vein? |
Drains O2 poor blood from the liver |
|
|
What is the function of the hepatic portal vein? |
Carries O2 poor but nutrient rich blood |
|
|
What is the function of the R & L hepatic ducts? |
Empties into common hepatic duct from R & L sides of liver |
|
|
What is the function of the common hepatic duct? |
Joins cystic duct from gallbladder |
|
|
What is the function of the cystic duct? |
Where content of gallbladder ejects into |
|
|
What is the function of the common bile duct? |
Drains into ampulla of Vater |
|
|
Where is the common bile duct located? |
Lesser omentum |
|
|
What is the function of the gallbladder? |
Store & then secrete bile into sm. intestine (under influence of CCK hormone) |
|
|
What are the functions of the lg. intestine? |
--Eliminates wastes & undigested minerals --(To a lesser degree) Continues reabsorption of H2O & vitamins |
|
|
What are haustra? |
Thin muscle fibers forming circular furrows (pouches) along ascending & transverse colons |
|
|
What is the function of haustra? |
Fill & distend via muscle contraction to move contents to next haustra |
|
|
What are taenia coli? |
Ribbons of smooth muscle on the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colons that produce haustral pouches |
|
|
What is the cecum? |
Small pouch that is the beginning of the lg. intestine |
|
|
What is the function of the cecum? |
Receives waste from the sm. intestine |
|
|
What separates the cecum from the ilium? |
Iliocecal valve |
|
|
What is the vermiform appendix? |
Blind-ended tube that is connected to the cecum |
|
|
What is the function of the vermiform appendix? |
Site of immune function |
|
|
What is the function of the colon? |
Moves waste from sm. intestine to rectum |
|
|
The colon is divided into how many segments (& what are they)? |
4 segments: --Ascending colon --Transverse colon --Descending colon --Sigmoid colon |
|
|
Approximately how long is the colon? |
6 ft. |
|
|
Where is the ascending colon? |
1st segment of lg. intestine that stems from cecum upward on the R side of body |
|
|
What is the transverse colon? |
2nd segment of lg. intestine that crosses abdomen from R to L |
|
|
What is the descending colon? |
3rd segment of lg. intestine that extends from the splenic flexure to the beginning of the sigmoid colon |
|
|
What is the function of the descending colon? |
Store food waste that will be emptied into the rectum |
|
|
What is the function of the sigmoid colon? |
Feces storage |
|
|
What is the R colic (hepatic) flexure? |
Bend in colon at juncture of ascending & transverse segments |
|
|
What is the L colic (splenic) flexure? |
Bend in colon at juncture of transverse & descending segments |
|
|
What is the function of the rectum? |
Stores feces |
|
|
What are the rectal (anal) columns? |
Vertical folds of mucous membrane at upper half of anal canal |
|
|
What are the rectal valves? |
Any of 3 or 4 crescent-shaped folds projecting into the rectal cavity
|
|
|
What is the internal anal sphincter? |
Smooth muscle that guard the anus |
|
|
What is the external anal sphincter? |
Skeletal muscle that guard the anus |
|
|
What are the hemorrhoidal veins? |
Any of several veins draining the walls of the anal canal & rectum |
|
|
What is the anus? |
Opening of anal canal to exterior |
|
|
What is the parietal peritoneum? |
Serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
What is the visceral peritoneum? |
Serous membrane that covers some organs in the abdominopelvic cavity & other serosa layer |
|
|
What are retroperitoneal organs vs. intraperitoneal organs? |
Retroperitoneal organs: --Organs posterior to abdominal wall (not in peritoneal cavity) --Not bound by mesentary Intraperitoneal organs: --Organs within peritoneal cavity |
|
|
What are the mesenteries of the gut? |
Bundles of extensions that anchor parts of the GI tract |
|
|
What is the greater omenum? |
Largest peritoneal fold from transverse colon down (AKA - the fatty apron) |
|
|
What is the lesser omentum? |
Attaches liver to diaphragm & anterior abdominal wall |
|
|
What is the mesentary proper? |
Cellophane-like anchor that binds jejunum & ilium |
|
|
What is the transverse mesocolon? |
Peritoneal folds binding transverse colon |
|
|
What is the mesoappendix? |
Mesentary of appendix that attaches appendix to inferior part of mesentary of ilium |
|
|
What are the general layers of the mucous membranes in the GI tract? |
--Epithelium (towards lumen) --Lamina propria --Muscularis mucosa |
|
|
What are the general layers of the muscularis externa comprised of? |
--Inner band of circular muscle fibers --Outter band of longitudinal muscle fibers |
|
|
What are Kupffer cells? |
Phagocytic cells forming the lining of liver sinusoids |
|
|
Where are Kupffer cells located? |
Sinusoids of liver |
|
|
What is the function of Kupffer cells? |
Phagocytic cells that break down RBCs |
|
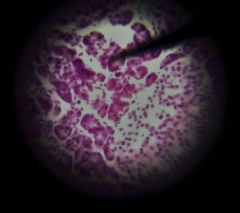
Identify this specimen |
Pancreas |
|
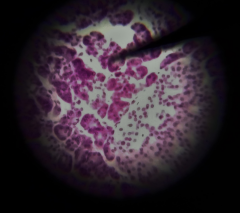
What are the structures at the tip of the pointer? |
Serous acini |
|
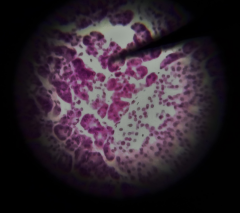
Does the structure at the tip of the pointer have an endocrine or exocrine function? |
Exocrine |
|
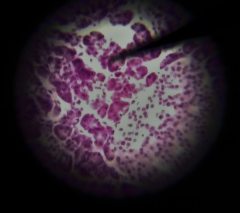
What is the function of the structure at the tip of the pointer? |
Secrete pancreatic juices with HCO3- and pancreatic enzymes |
|
|
What are some of the pancreatic enzymes? |
--Lipase --Amylase --Trypsin --Chymotrypsin --Caboxypeptidase --Elastase --Nuclease |
|
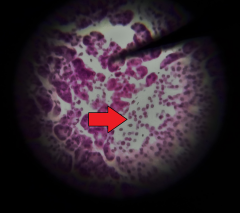
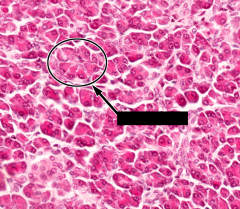
What is the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Pancreatic islet (AKA - islet of Langerhans) |
|
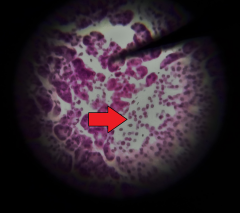
Do the cells of the structure at the tip of the red arrow have an endocrine or exocine function? |
(Pancreatic islet or Islet of Langerhans) Endocrine |
|
|
Identify 2 cells located in the pancreatic islet (islet of Langerhans) and what each cell secretes |
--Alpha cells secrete glucagon --Beta cells secrete insulin |
|
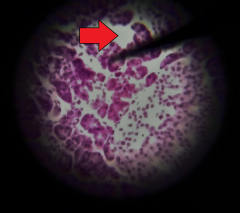
What is the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Interlobular duct |
|
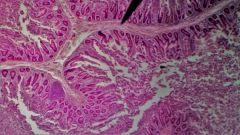
Identify the specimen |
Jejunum |
|
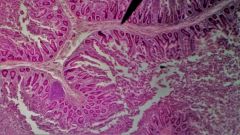
Identify the layer at the tip of the pointer |
Submucosa |
|
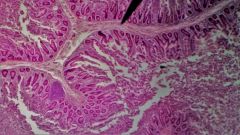
Identify the entire fold at the tip of the pointer |
Plica circularis |
|
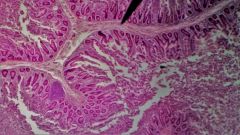
What is the function of the fold at the tip of the pointer? |
Increase surface area for absorption |
|
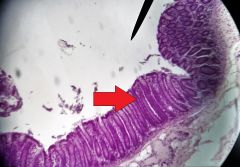
What is the white linear structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Intestinal gland (AKA - crypt of Lieberkühn) |
|
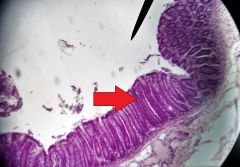
Identify the cells at the tip of the red arrow |
Goblet cells |
|
|
What is the function of goblet cells? |
Secrete mucous |
|
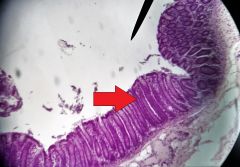
What is the entire layer the red arrow is pointing to? |
Mucosa |
|
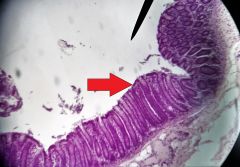
What is the tissue lining the lumen? |
Simple columnar epithelial tissue |
|
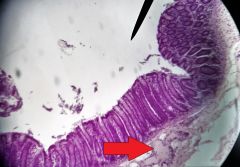
What specific layer is the red arrow pointing to? |
Submucosa |
|
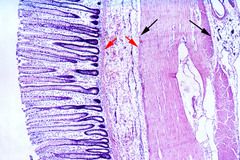
What layer are the black arrows pointing to? |
Muscularis (inner layer of circular fibers; outter layer of longitudinal fibers) |
|
|
What is the function of the muscularis? |
Haustral churning/peristalsis |
|
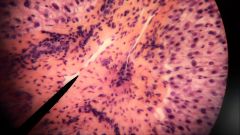
What is the specific specimen? |
Liver |
|
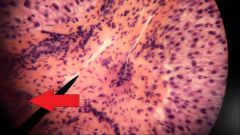
What is the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Hepatic artery |
|
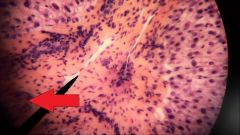
What fluid is found in the structure at the top of the red arrow? |
Oxygen rich blood
|
|
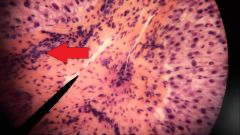
What is the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Bile duct |
|
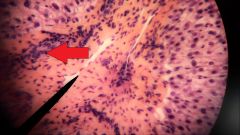
What fluid is found in the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Bile |
|
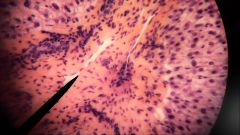
What structure is found at the tip of the pointer? |
Branch of hepatic portal vein |
|
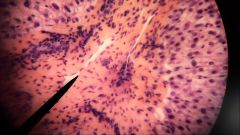
What fluid is found in the structure located at the tip of the pointer? |
Oxygen poor, nutrient rich blood (may have toxins) |
|
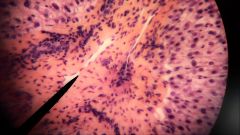
Identify these cells |
Hepatocytes |
|
|
What are some of the functions of hepatocytes? |
--Secrete bile --Metabolize lipids, carbs, & proteins --Detoxification |
|
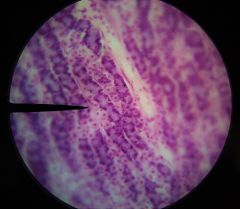
What is the specimen shown? |
Fundic stomach |
|
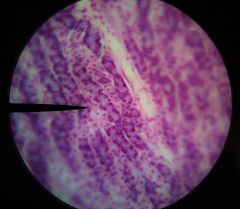
What is the specific layer in the field of view? |
Mucosa |
|
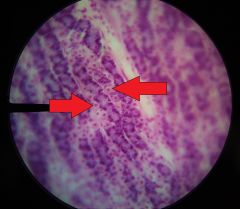
What are the specific cells at the tips of the red arrows (right of pointer)? |
Parietal cells |
|
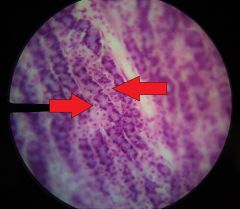
What substances are secreted by the cells at the tips of the red arrows? |
--HCl --Intrinsic factor |
|
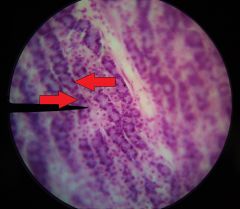
What specific cells are at the tips of the red arrows (left of pointer)? |
Chief cells |
|
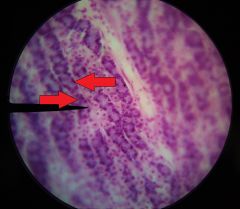
What substances are secreted by the cells at the tips of the red arrows? |
--Pepsinogen --Gastric lipase |
|
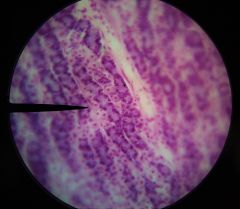
What is the long structure at the tip of the pointer that these cells are a part of? |
Gastric gland |
|
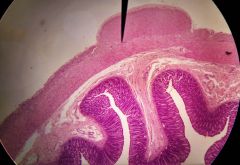
Identify the layer at the tip of the pointer |
Muscularis |
|
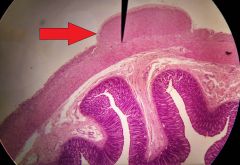
Identify the specific layer at the tip of the red arrow |
Serosa |
|
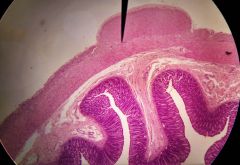
Identify the specific structure at the tip of the pointer |
Myenteric plexus |
|
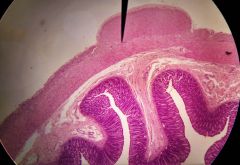
What is the function of the structure at the tip of the pointer? |
Regulating motility by regulating muscularis |
|
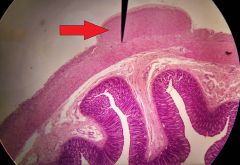
What is the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Tenia coli |
|
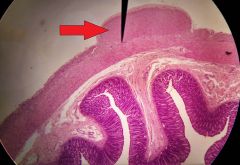
What is the specific layer at the tip of the red arrow? |
External longitudinal layer of muscularis |
|
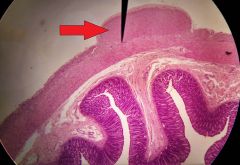
What is the function of the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Peristalsis |
|
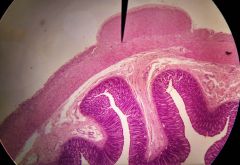
What is the lighter staining region shown? |
Submucosa |
|
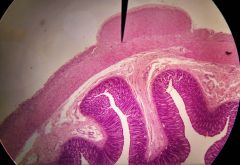
What specific tissue is found in the lighter staining region shown? |
Areolar connective tissue |
|
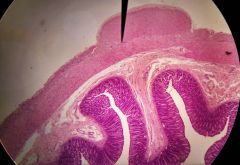
Identify the structures that look like white stripes |
Intestinal glands (AKA - crypts of Lieberkühn) |
|
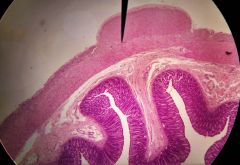
What is the specimen shown (& how can you tell)? |
Colon --Crypts of Lieberkühn --No gastric pits or villi --Tenia coli |
|
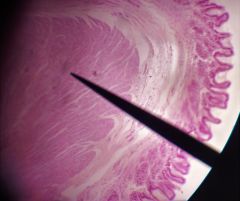
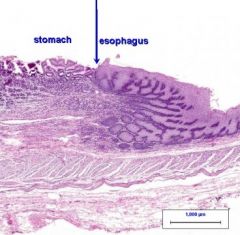
What is the specimen shown? |
Gastroesophageal junction |
|
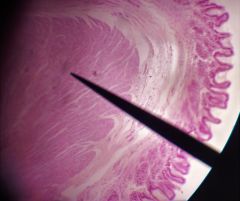
Identify the structure at the tip of the pointer |
Lower esophageal sphincter (AKA - cardiac sphincter) |
|
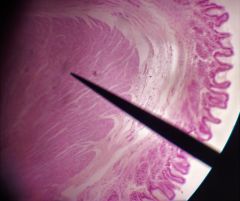
What are the functions of the structure at the tip of the pointer? |
(Lower esophageal sphincter) --Allow bollus into stomach --Prevent reflux of acid from stomach into esophagus |
|
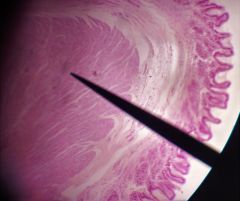
What is the specific layer at the tip of the pointer? |
Inner circular layer of muscularis |
|
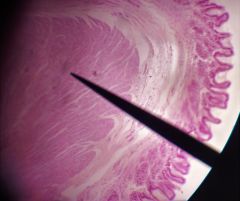
What specific tissue is found at the tip of the pointer? |
Smooth muscle tissue |
|
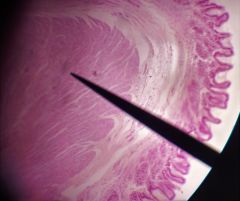
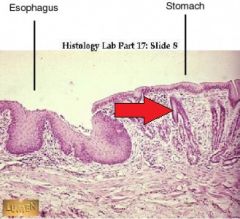
Stomach or esophagus? |
Stomach |
|
|
What specific type of tissue lines the lumen of the esophagus? |
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelial tissue (NKSSET) |
|
|
What specific type of tissue lines the lumen of the stomach? |
Simple columnar epithelial tissue |
|
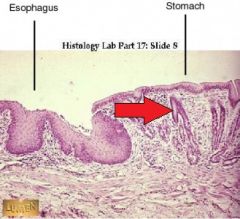
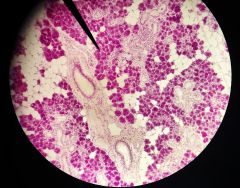
What is the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Mucous glands |
|
What is the function of the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Secrete mucous |
|
What is the specimen shown? |
Submandibular gland |
|
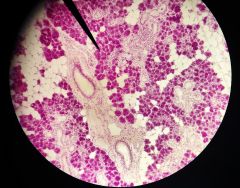
What are the structures at the tip of the pointer? |
Serous acini |
|
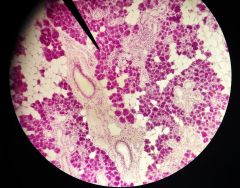
What is the function of the structures at the tip of the pointer? |
Secrete watery saliva with salivary amylase |
|
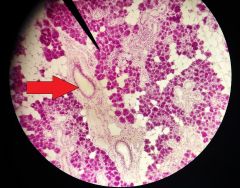
What is the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Interlobular duct |
|
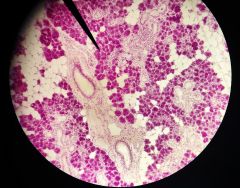
What is the structure to the right of the pointer? |
Mucousal tubule |
|
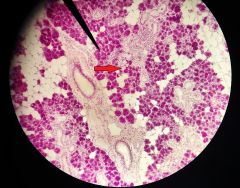
What is the function of the structure to the right of the pointer? |
(Mucousal tubule) Secrete mucous saliva |
|
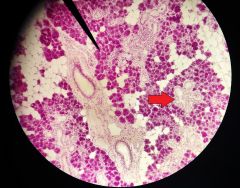
What is the structure at the tip of the red arrow? |
Intralobular duct |
|
What is the structure at the tip of the pointer? |
Mucuous tubule |
|
What is the function of the structure at the tip of the pointer? |
Secrete mucous saliva |
|
What are the darker staining structures surrounding the duct at the tip of the pointer? |
Serous acini |
|
What is secreted by the darker staining structures surrounding the duct at the tip of the pointer? |
(Serous acini) secrete salivary amylase |
|
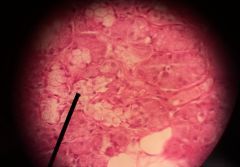
Identify the lighter purple staining structures
|
Intralobular ducts |
|
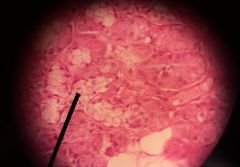
Identify the specimen (& how can you tell)? |
Submandibular gland --Serous acini & mucous tubules --No skeletal muscle |
|
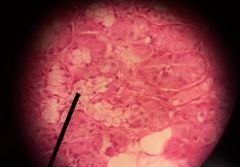
What is the function of the specimen shown? |
Secrete a mixture of watery saliva & mucous saliva |
|
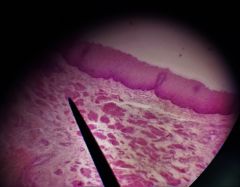
What is this specimen? |
Esophagus |
|
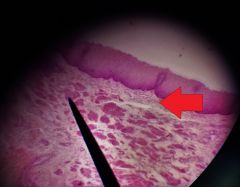
What is the specific layer at the tip of the red arrow? |
Lamina propria |
|
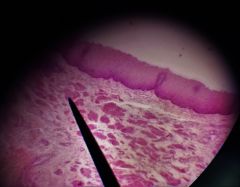
What is the specific layer at the tip of the pointer? |
Muscularis mucosa |
|
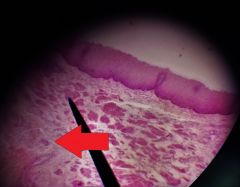
What is the specific layer at the tip of the red arrow? |
Submucosa |
|
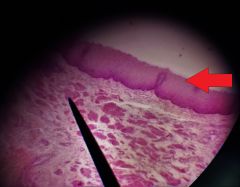
What specific tissue type is at the tip of the red arrow? |
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelial tissue |
|
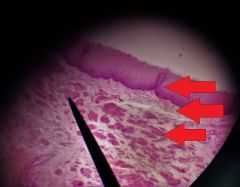
What layer is formed by the 3 tissue types located at the tips of the red arrows? |
Mucosa |
|
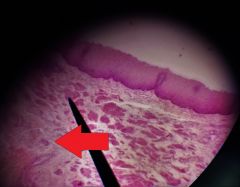
What layer lies directly below the layer shown at the tip of the red arrow? |
Muscularis |
|
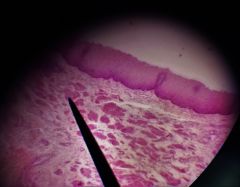
Below the muscularis on this specimen, would you expect to find adventitia or serosa? |
Adventitia |
|
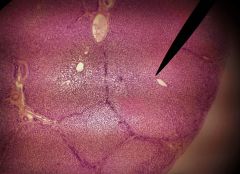
What is the specimen shown? |
Liver |
|
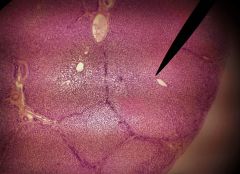
What is the structure shown at the tip of the pointer? |
Central vein |
|
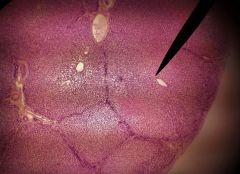
Identify the cells surrounding the pointer |
Hepatocytes |
|
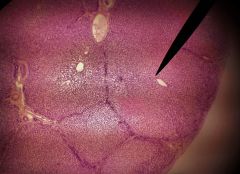
Identify the functions of the cells surrounding the pointer |
(Hepatocytes) --Secrete bile --Metabolize lipids, carbs, & proteins --Detoxification |
|
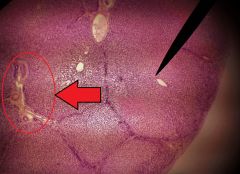
What is the collective name of the structures circled in red? |
Portal triad |
|
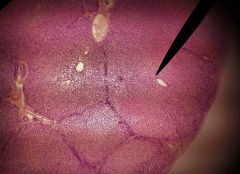
Would you expect to find adventitia or serosa surrounding much of the specimen shown? What is the function of this layer? |
Serosa; Provides lubrication to reduce friction |
|
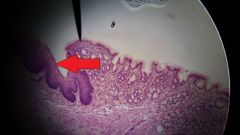
What is the organ at the tip of the red arrow? |
Esophagus |
|
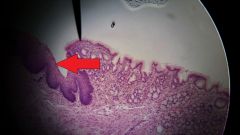
What specific type of tissue is found at the tip of the red arrow? |
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelial tissue |
|
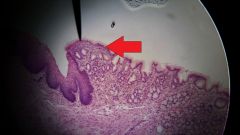
What organ is found at the tip of the red arrow? |
Stomach |
|
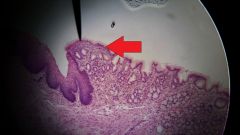
What specific tissue type is found at the tip of the red arrow? |
Simple columnar epithelial tissue |
|
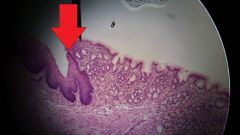
What feature is found at the tip of the red arrow? |
Gastroesophogeal junction |
|
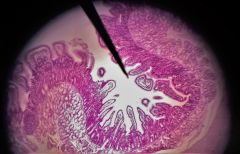
Identify the structure shown |
Duodenum |
|
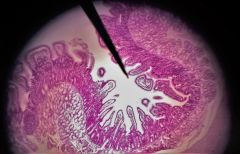
Identify the finger-like structure at the tip of the pointer |
Villus |
|
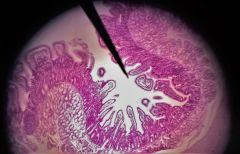
Identify the entire fold/structure at the tip of the pointer |
Plica circularis |
|
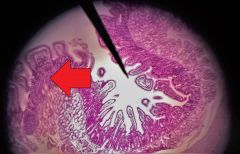
Identify the dark purple structures |
Crypts of Lieberkühn |
|
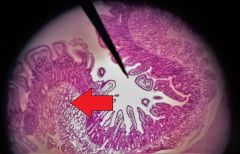
Identify the structures at the tip of the red arrow |
Duodenal glands |
|
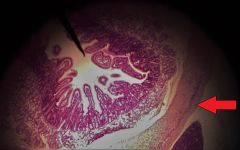
What is the specific layer at the tip of the red arrow? |
Outer longitudinal layer of muscularis |
|
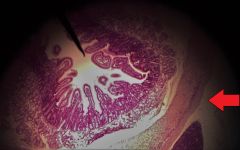
Identify the specific layer at the tip of the red arrow |
Adventitia |
|
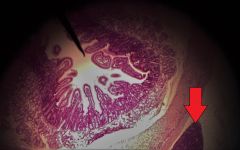
What is the organ at the tip of the red arrow? |
Pancreas |
|
|
What is deglutition? |
The act of swallowing |
|
|
What are the 3 stages of deglutition? |
--Voluntary: act of tongue forcing bolus against hard palate & into oropharynx --Pharyngeal: bolus passes into oropharynx --Esophageal: bolus enters esophagus & moves towards stomach |
|
|
What is GERD? |
Gastroesophageal reflux disease: incompetent lower esophageal sphincter allows stomach acid into esophagus |
|
|
What is the function of intrinsic factor? |
Allows body to absorb vitamin B12 |
|
|
Approximately how much pancreatic juice is secreted per day? |
1 - 1.5 L |
|
|
Approximately how much saliva is secreted per day? |
1 - 1.5 L |
|
|
What is the function of insulin? |
Decrease blood sugar |
|
|
What is the function of glucagon? |
Increase blood sugar |
|
|
What is the function of sodium bicarbonate (in GI tract)? |
Gives pancreatic juice slightly alkaline pH which acts as buffer
|
|
|
What is the function of amylase? |
Starch digesting enzyme |
|
|
What are some of the enzymes that break down proteins into peptides? |
--Peptidase --Trypsin --Chymotripsin |
|
|
What is the function of pancreatic lipase? |
Triglyceride digesting enzyme in adults |
|
|
What are the enzymes that break down DNA & RNA into nucleotides? |
--Ribonuclease --Dioxyribonuclease |
|
|
What is another term for hypomotility of the lg. intestine? |
Constipation |
|
|
What is another term for hypermotility of the lg. intestine? |
Diarrhea |
|
|
What are the 3 phases of digestion? |
--Cephalic phase --Gastric phase --Intestinal phase |
|
|
What are the stimuli that initiate the cephalic phase of digestion? |
Smell, sight, thought, or taste of food |
|
|
What occurs during the cephalic phase of digestion? |
Secretion of saliva & gastric juices |
|
|
What is the stimulus that initiates the gastric phase of digestion? |
Food enters stomach |
|
|
What occurs during the gastric phase of digestion? |
--Gastrin promotes secretion of gastric juice & increases gastric motility while relaxing pyloric sphincter --Acidic chyme enters duodenum |
|
|
What are the stimuli that initiates the intestinal phase of digestion? |
--Acidic chyme enters sm. intestine
--Duodenal stretch receptors --(CCK) Detection of amino acids & lipids --(Secretin) Decreased pH |
|
|
What occurs during the intestinal phase of digestion? |
--Duodenal stretch receptors stimulate sympathetic N.S. to inhibit gastric motility & inhibit pyloric sphincter --CCK stimulates pancreatic & gallbladder secretion & contracts pyloric sphincter --Secretin stimulates pancreatic secretion & inhibits gastric secretion |
|
|
What is the function of the electron transport chain? |
Extract energy stored in reduced co-enzymes (i.e., NADH & FADH2) |
|
|
What are the 4 stages of ATP production & where does each occur? |
--Glycolysis (cytoplasm) --Formation of Acetyl-CoA (mitochondrial matrix) --Krebs (mitochondrial matrix) --ETC (inner membrane) |
|
|
What is lipid catabolism? |
Breakdown of lipids |
|
|
What is lipolysis? |
Oxidation of lipids to yield glucose (to then yield ATP) |
|
|
What is beta oxidation? |
Process of cleaving off 2-carbon fragements from long fatty acid chains that occurs in mitochondrial matrix |
|
|
What are ketone bodies? |
Any of 3 ketoacid compounds produced during the metabolism of fats |
|
|
What is ketogenesis? |
Normal part of fat breakdown that causes metabolic acidosis when in excess |
|
|
What is ketoacidosis? |
State of decreased pH due to excessive ketone body buildup |
|
|
What is acetone? |
Ketone body that produces sweet smell to someone's breath (symptom of ketoacidosis) |
|
|
What is "bad cholesterol" & why is it bad? |
LDL: when produced excessively the cholesterol carried outnumbers bodily need, so cholesterol is just "dumped" along the way & accumulates in arteries |
|
|
What is "good cholesterol" & why is it good? |
HDL: removes excess cholesterol "dumped" by LDL & transports it to the liver for elimination from the body |
|
|
What is a chylomicron? |
A droplet of fat present in the blood or lymph after absorption from the small intestine |
|
|
What is protein catabolism? |
Proteins are broken down into amino acids to produce ATP or synthesize new proteins |
|
|
What happens to excess amino acids in the body? |
Converted into glucose (glucogenesis) or triglycerides (lipogenesis) |
|
|
What is deamination? |
Removal of an amino group leaving the carbons of a carboxylic acid to be used to make ATP |
|
|
What is transamination? |
Transfer of an amino group (NH2) to pyruvic acid or other acid in Krebs cycle to form amino acid (protein anabolism) |
|
|
Where & how is urea formed? |
Ammonia is produced in the liver & converted to urea to be excreted in urine |
|
|
What is cellular respiration? |
Process that converts biochemical energy into ATP |
|
|
What is phosphorylation? |
Adding a phosphate group to a molecule |
|
|
How can glucose be used in the body? |
--ATP production --Amino acid synthesis --Glycogen synthesis (liver & muscle cells) --Triglyceride synthesis (lipogenesis) |
|
|
What is the function of PFK? |
Regulates the rate at which glycolysis can occur |
|
|
What is oxidation? |
Loss of electron from substance (reducing agent) |
|
|
What is reduction? |
Gain of electron from substance (oxidizing agent) |
|
|
What is the aerobic cellular respiration chemical equation? |
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 36 or 38 ADP + 36 or 38 P --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 or 38 ATP
|
|
|
What are the anabolic reactions of the body? |
--Glycogen synthesis --Amino acid synthesis --ATP production --Triglyceride synthesis |
|
|
What is the main catabolic reaction of the body? |
Digestion |
|
|
What are 3 types of lipase? |
--Lingual --Gastric --Pancreatic |
|
|
What are the secreting cells of the stomach & what do they secrete? |
--Parietal cells (intrinsic factor) --Chief cells (pepsinogen & gastric lipase) --Mucous cells (mucous) --Mucous neck cells (mucous) --G cells (gastrin) |
|
|
What is the GI tract? |
Lumen extending from oral cavity to anus |
|
|
What are the segments of the GI tract? |
--Oral cavity --Laryngopharynx --Esophagus --Stomach --Duodenum --Jejunum --Ilium --Ascending colon --Transverse colon --Descending colon --Sigmoid colon --Rectum --Anus |
|
|
What are the accessory organs of the digestive system? |
--Tongue --Teeth --Salivary glands --Gallbladder --Pancreas --Liver |
|
|
What are the 6 functions of the digestive system? |
--Ingestion --Secretion --Mixing & propulsion --Digestion --Absorption --Defecation |
|
|
Approximately how much fluid issecreted into the GI tract per day? |
7 L |
|
|
What is motility? |
Movement of food/waste through GI tract |
|
|
What are the 2 types of motility? |
--Propulsion --Segmentation |
|
|
What is propulsion? |
Movement of material through GI tract via peristalsis |
|
|
What is segmentation? |
Localized mixing contractions in portions of the sm. intestine distended by chyme |
|
|
What is MMC? |
Migrating motility complex, a type of peristalsis in sm. intestine that propels chyme |
|
|
What are the 2 types of digestion? |
--Mechanical digestion --Chemical digestion |
|
|
What is mechanical digestion? |
Chewing food to increase surface area & mix with enzymes |
|
|
What is chemical digestion? |
Breakdown of food into usable resources by the body |
|
|
What substances are found in saliva? |
--Salivary amylase --Lingual lipase --H2O --Mucous --Lysozymes --Ions |
|
|
What is the esophageal hiatus? |
The opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes |
|
|
What are the functions of the stomach? |
--Mixes saliva, food, & gastric juice (chyme) --Reservoir for food --Secretion (gastric juice, gastric lipase, & intrinsic factor) |
|
|
What is the function of HCl in digestion? |
--Kills bacteria --Denatures proteins |
|
|
What is the function of pepsin in digestion? |
Begins digestion of proteins |
|
|
What is the function of gastric lipase in digestion? |
Aids digestion of triglycerides |
|
|
What is the function of the ETC? |
Extract energy stored in reduced co-enzymes formed during previous stages of cellular respiration |
|
|
What is chemiosmosis? |
Movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane down an electrochemical gradient |
|
|
What are the steps of chemiosmosis? |
1. Energy from NADH-H+ passes along ETC & used to pump H+ ions into space between inner & outer membranes 2. High concentration of H+ accumulates in this space 3. ATP synthesis occurs as H+ flows back into matrix thru a H+ channel that includes ATP synthase |
|
|
Approximately how much bile is secreted per day? |
1 L |
|
|
What is the function of bile? |
Emulsifies fats for watery environment of sm. intestine digestive juices |
|
|
What is the functional unit of the liver? |
Hepatic acinus |
|
|
What are the 4 types of jaundice & their causes? |
--Prehepatic jaundice: excess production of bilirubin --Hepatic jaundice: due to congenital liver disease, cirrhosis of liver, or hepatitis --Extrahepatic jaundice: due to blockage of bile drainage by gallstones or cancer to bowels or pancreas --Neonatal jaundice: mild jaundice in newborns due to immature functioning of liver |
|
|
What are the functions of the sm. intestine? |
--Mechanical digestion (segmentation) --Chemical digestion (brush border enzymes) --Absorption (90%) |
|
|
Approximately how much intestinal juice is secreted per day? |
1 - 2 L |
|
|
What are the brush border enzymes? |
--α-dextrinase --Maltase --Sucrase --Lactase --Peptidase --Nucleosidases --Phosphatases |
|
|
What are the pancreatic enzymes? |
--Pancreatic amylase --Pancreatic lipase --Trypsin --Chymotripsin --Peptidase --Ribonuclease --Deoxyribonuclease |
|
|
What causes lactose intolerance? |
Absorbtive cells of sm. intestine fail to make enough lactase |
|
|
What is lactose intolerance? |
Undigested lactose in chyme causes fluid retention in feces & bacterial fermentation of undigested lactose |
|
|
What are the symptoms of lactose intolerance? |
After consumption of milk & dairy products --Diarrhea --Gas/bloating --Abdominal cramps |
|
|
What substance is required to absorb Ca2+? |
Calcitrol |
|
|
What are the 3 reflexes of defecation? |
--Gastroilial reflex pushes chyme into cecum --Gastrocolic reflex pushes contents of colon into rectum --Defecation reflex triggered by stretch receptors in rectum |
|
|
What are the steps of defecation? |
--Food in stomach triggers mass peristalsis --Chyme moves through intestines to rectum --Rectal pressoreceptors respond to distension --ANS releases internal anal sphincter & gives conscious awareness of distension |
|
|
What makes feces brown? |
Bilirubin from catabolized RBCs |
|
|
What is the enterogastric reflex? |
Reflex inhibiting stomach emptying contents when duodenum is obstructed, overfilled, or irritated |
|
|
What is metabolism? |
Net sum of all body reactions |
|
|
What is catabolism? |
Breaking down lg. molecules into sm. molecules |
|
|
What is anabolism? |
Building up sm. molecules into lg. molecules |
|
|
What are NAD+ & FAD? |
Intermediate coenzymes (& B vitamins) that can accept transfer of e- until ADP can be transformed into ATP |
|
|
What are NADH & FADH2? |
Intermediate coenzymes that have accepted transfer of e- & are temporarily storing harvested bond energy until ADP can transforminto ATP |
|
|
What are 4 types of lipoproteins? |
--Chylomicron --VLDL --LDL --HDL |
|
|
What is the body's main concern during the absorptive state? |
Producing ATP by oxidizing glucose |
|
|
What is the body's main concern during the postabsorptive state? |
Maintaining homeostasis of blood glucose levels for neurons & RBCs |
|
|
What is gluconeogenesis? |
Synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrates |
|
|
What is the function of ATP? |
Biochemical way to use & store energy ("energy currency" of the body) |

