![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Evolution |
Darwin said “Descent with modification” Can be both A pattern and a process Origin of species 1859 |
|
|
Earths many species are ancestors of earlier species |
Evolution Creating diversity, unity, and adaptations |
|
|
Aristotle |
Greek Believed Scala naturae (ladder of increasing complexity) many species were permanent and unchanging Believed species were made by god so they were perfect |
|
|
Linnaeus |
Organismal adaptations as evidence the a creator had designed each species for a specific purpose Grouped species together= binomial Founder of taxonomy (classifying organisms) |
|
|
Fossils |
Traces of organisms from past Found in strata Helped Darwin lay groundwork |
|
|
Paleontology |
Study of fossils Developed by Georges Cuvier who Believed strata (layers of earth) represented catastrophic events Saw in layer to layer-species appeared and disappeared so supported extinction but did not support evolution |
|
|
Hutton and Lyell |
Geologists Hutton Believed in gradualism (changes to environment like rivers were slow over time) Lyell added that gradualism continues to occur which he called (uniformiterism) |
|
|
Jean Baptiste de Lamarck |
Believed in evolution and that species evolved through use and disuse of body parts And believed inheritance of acquired characteristics Giraffe neck example |
|
|
Darwin |
Naturalist Studied medicine but decided to study theology Traveled around the world with FtizRoy on the beagle for 5 years |
|
|
Voyage of the beagle |
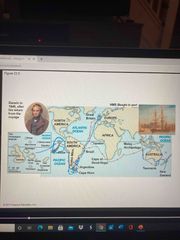
Darwin collected specimens of South America plants and animals Observed fossils that resembled living species from the same region and other fossils resembled other species from nearby areas Earthquake in Chile observed where rocks were uplifted Hypothesized that species from South America had colonized the Galapagos and speculated in the islands |
|
|
Darwin’s adaptation focus |
Animals were fit to their environment Example of beaks of finches |
|
|
Natural selection |
1844 mechanism of descent with modification but feared publication Individuals with favorable inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce 1858: receives manuscript from Wallace with similar idea and decided Darwin should own it. Darwin write the Origin of species |
|
|
Immaculate logic’s and avalanche of evidence for |
Evolution |
|
|
Origins of species |
Unity of life Diversity of life The ways organisms are suited to life in their environment Did not mention word evolution |
|
|
History of life is like a tree with branches |
Large morphological gaps btw related species could be explained by branching process and past extinction events |
|
|
Artificial selection |

Used this to start to describe how natural selection occurs Humans have modified other species by selecting and breeding desired traits |
|
|
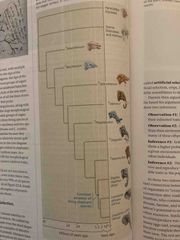
Observations and inferences |
Ob 1: members of population vary in inherited traits (ladybug spots) Ob 2: all species can produce more offspring than the environment can support and many fail (spores from fungus) Infer 1: individuals whose inherited traits give them higher chance of surviving and reproducing in an environment Infer 2: this leads to accumulation of favorable traits over time (think of darker beetles) |
|
|
Malthus |
Noted potential for human population to increase faster than food supplies and resources which led to human suffering (war, famine, disease) Favorable adaptations and continue to reproduce and pass on genes |
|
|
3 key features of natural selection |
1. Individuals do not evolve, populations do 2. Natural selection can amplify or diminish traits. Think about only inheritable traits 3. Environmental factors impact which adaptations continue |
|
|
4 categories supporting evolution |
1. Direct observations 2. Homology 3. Fossil record 4. Biogeography
|
|
|
2 examples of observations |
1. Natural selection in response to introduced species 2. Evolution of drug-resistant bacteria |
|
|
Natural selection in introduced species |
Soap berry bugs eat seeds in fruit with beaks Most effective if beak length is equal to seed depth Feed on balloon vine have longer beaks in southern FL and in central FL, feed on golden rain tree have shorter beaks |
|
|
An inheritance trait... |
Length of beak in soap bugs |
|
|
Drug-resistant bacteria |
Staphylococcus is found all over us One strain, MRSA has become dangerous 1945: 2 years resistant to penicillin 1961: 2 yrs resistance to methicillin |
|
|
Methicillin |
Inhibits enzyme in bacteria to create cell wall Evolved to use a different enzyme mRSA is nonresistant |
|
|
Natural selection does not create new traits... |
It selects more favorable traits. Ex: Think of Beatles that are dark and light. Dark was always there The environment determines which traits will be selected for or against and it can be rapid within a few years/decades |
|
|
Homology |
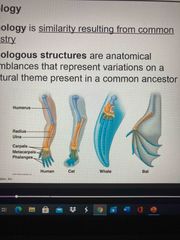
Similarities and characteristics btw different organisms Result from common ancestor |
|
|
Homologous structures |
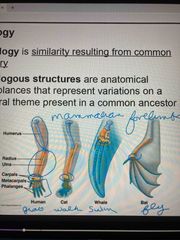
Anatomical structures resemble each other structurally with some variation Ex: all have Digits-human, cat, what, bat but are for different function, yet share shape and structure |
|
|
Embryology |
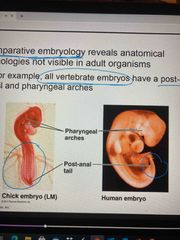
Comparative: compares embryos of different species All vertebrae embryos have a post-anal tail |
|
|
Vestigial structures |
Remnants of features that served a function in the organisms ancestor but does not now Ex: pelvis bones in snakes and whales |
|
|
Homologous at the molecular level |
Genes among organisms inherited from a common ancestor If studying a gene, have to say percentage of how shared the gene is btw organisms |
|
|
Evolutionary trees |
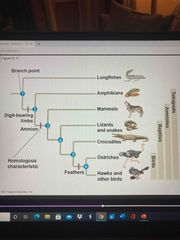
Diagrams that reflect hypothesis about the relationships among groups Can be made using different types of data |
|
|
Homologous form——in evolutionary trees |
Nested patterns |
|
|
Convergent evolution |

Analogous or similar features in distant related groups They independently adapt in similar environments in similar ways Does not provide info about ancestry |
|
|
Does not provide info about ancestry... |
Convergent evolution Ex: glider and flying squirrel most common ancestor does not share the skin flap. It is analogous. They developed independently |
|
|
4. Fossil record evidence |
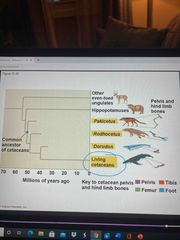
Provides evidence of extinction, origin of new groups, and changes over time Can document important transitions Ex: transition from land to sea in the ancestors of cetaceans |
|
|
Fossil evidence also shows... |
Living cetaceans and their close relatives are more different from each other today than they were early ones |
|
|
Biogeography |
Study of geographic distribution of species Provides evidence of evolution All continents, Pangaea, were one 200 million years ago Over time separated and understanding this has allowed us to predict where and when species evolved Ex: horses originated in North America |
|
|
Endemic |
Species not found anywhere else Often on islands Closely related to main land species, adapted, and have rise to new species |
|
|
Theory in science |
Accounts for many observations and data Natural selection is a theory just like gravity Ongoing research adds to our understanding Ex: actually faster than Darwin once thought |

