![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cancer results from genetic changes that affect cell cycle control |

Gene regulation system that goes wrong during cancer are the the same systems involved in embryonic development (Mutations to gene that normally regulate cell growth and division) Spontaneous mutations or environmental influences can cause cancer (chemicals, radiation, viruses) |
|
|
Proto-oncogene |
Genes responsible for normal cell growth and division Conversion of these leads to an oncogene |
|
|
Oncogenes |
Cancer-causing genes in some types of viruses |
|
|
There are 3 ways in which proto-oncogenes can be converted. |
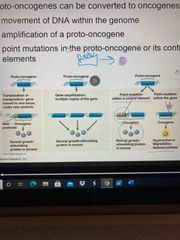
1. Movement of DNA within the genome 2. Amplification of a proto-oncogene 3. Point mutation in pg or in its control elements All lead to too much growth stimulating protein |
|
|
Tumor-suppressor genes |
Normally inhibit cell division Repair DNA damage (remove chunk that needs replaced) Control cell adhesion (density) Act in cell-signaling pathways that inhibit the cell cycle |
|
|
Mutations that decrease protein products of____may contribute cancer onset |
Tumor-suppressor genes Cell check points P53 example |
|
|
Mutations in these genes are common in cancers |
ras proto-oncogene and p53 tumor suppressor gene 30% cancers due to mutation in ras gene 50% cancers due to p53 mutation |
|
|
Ras gene |
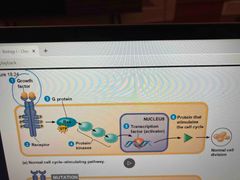
G protein that relays a signal from growth factor receptor on cells surface The response to the resulting cascade stimulates cell division Tumor-suppressor |
|
|
A mutation in ras gene leads to.. |
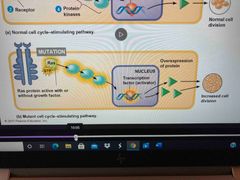
Hyperactive ras protein which increases cell division |
|
|
P53 gene |
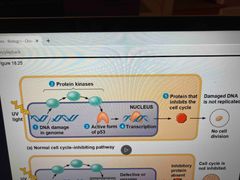
Prevents cell from passing on mutations when a cells DNA is damaged It activates expression of miRNA that inhibit the cell cycle and turns on genes that are involved in repair If dna cannot be repaired, activates apoptosis genes |
|
|
If mutation in p53 gene... |
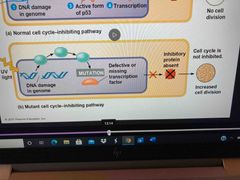
Prevents suppression of cell cycle which can lead to continue dividing of damaged DNA, passing on mutations |
|
|
To develop full-fledged cancer.. |
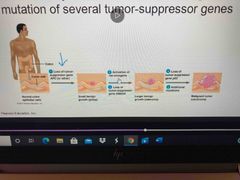
You need multiple mutations A cancer cell is usually characterized by one active oncogene and the mutation of several other tumor-suppressor genes Multiple Hit-hypothesis |
|
|
Routine screening for some cancers is recommended |
Colorectal cancer Suspicious polyps may be removed before cancer progresses |
|
|
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease |
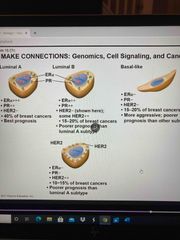
2nd most common cancer in women 4 major types from a genomics approach |
|
|
Individuals can inherit oncogenes or mutant alleles of tumor-suppressor genes |
In colon cancer: inherited mutations in tumor-suppressor gene (APC) In breast cancer: mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene are found in at least half of inherited cancers |
|
|
A number of tumor viruses can also cause cancer in humans and animals |
Viruses can interfere with normal gene regulation in several ways (donate a oncogene, promote multiple copies, can activate p53) Viruses are powerful biological agents ie: HPV |

