![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
180 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Translocation |

Type of chromosome structure breakage Moves a segment from one chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome Typical harmful |
|
|
Parallels made early on |
Chromosomes and genes are both present in pairs in diploid cells Homologous chromosomes separate and alleles segregate during meiosis Sister chromatids separate to form 4 haploid gamete cells Fertilization restores the paired condition for chromosome and genes |
|
|
Chromosome theory of inheritance |
Genes occupy specific loci on chromosomes Chromosomes undergo segregation and independent assortment during meiosis Homologous chromosomes accounts for segregation of the alleles at each genetic locus to different gametes Nonhomologous chromosomes account for independent assortment of alleles for 2 or more genes on different chromosomes |
|
|
First to provide evidence of a specific gene on a specific chromosome |
Thomas hunt Morgan, 1900s Mated fruit flies |
|
|
Fruit flies are good to use bc |
Produce many offspring Generation bred every 2 weeks 4 pairs of chromosomes (3 autosomes and a pair of sex chromosomes) |
|
|
Wild type ( w+ ) |
Common in the “wild” was red eyes-phenotype that is more common Mutant phenotype is alternative to the wild type ( white eyes instead of red) |
|
|
Correlating behavior of a genes alleles with behavior of a chromosome pair |

Morgan mated male (XwY) with white eyes with female (Xw+Xw) with red eyes F1 gen all red eyes F2 gen 3:1 ratio but only males had white eyes |
|
|
Morgan determined that white-eyes mutant allele must be located on the... |
X chromosome |
|
|
How many varieties of sex chromosomes in humans and mammals? |
2: X and Y XX= female, XY=male Short segments at the ends of Y chromosomes are homologous with the X allowing the two to behave like homologous during meiosis in males |
|
|
A gene on Y chromosome is called... |
SRY (sex determining region on the Y) responsible for development of testes in an embryo (1990) |
|
|
How many genes on Y chromosomes? |
78 genes codes for about 25 proteins Half are expressed only in tested and some are required for normal testicular function and the production of normal sperm |
|
|
Sex-linked gene |
Gene located on either sex chromosome Genes on Y chromosomes are Y-linked genes (few of these) Genes on X chromosome are X-linked genes (contains about 1100) |
|
|
X chromosomes have genes for many characters unrelated to... |
Sex Y-link genes are related to sex |
|
|
Passing X-linked alleles |
Fathers pass x-linked alleles to all their daughters but none of their sons Mothers can pass to both sons and daughters |
|
|
For a recessive X-linked trait to be expressed... |
A female needs two copies of the allele (homozygous) Heterozygous females are carriers A male needs only one copy of the X allele (hemizygous) Much more common in males than females |
|
|
Color blindness X-linked |

Females need 2 recessive alleles Male only one recessive allele Females can be carriers |
|
|
Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
Due to absence of x-linked gene called dystrophin (muscle protein) Characterized by a progressive weakening of the muscles and loss of coordination Rarely live past 20s |
|
|
Hemophilia |
Deficiency blood clotting factor Prolonged bleeding bc firm clots form slowly 1800s widespread in royal families in Europe |
|
|
X inactivation |
In female mammals, one of the two X chromosomes in each cell is randomly inactivated during embryonic development Inactive X is Barr body |
|
|
Barr body |
Condensed inactive X chromosome. Reactivated in ovarian cells that produce eggs |
|
|
If female is heterozygous for a particular gene located on the X chromosome, she will be a |
Mosaic for the character |
|
|
Mary Lyon |
British geneticist Barr body occurs randomly and independently in each embryonic cell Females consist of a mosaic of two types of cells (some with active paternal X and others with active maternal X) |
|
|
After an X chromosome is inactivated |
All mitotic descendants of that cell will have the same inactive X heterozygous for a sex-linked trait female will have half her cells express one allele and the other half the other allele mosaic for that character ie: heterozygous for an Xlinked mutation that prevents the development of sweat glands |
|
|
X inactivation involves modification of... |
The DNA and the histone proteins by attachment of a methyl (CH3) group to one of the nitrogenous bases of DNA One of these genes (XIST) becomes active only in Barr chromosome Copies of RNA attach to X chro. Almost covering it |
|
|
XIST X-inactive specific transcript |
Gene that is activated when methyl group binds to DNA base modifying DNA and histones This gene becomes active on Barr-body chromosome RNA of XIST gene attach to X chro. On which they are made, covering it Inactivated X while RNA products help regulate |
|
|
Linked genes tend to be inherited together because... |
They are located near each other on the same chromosome |
|
|
Number of linked genes versus recombinant |
83% verses 17% Freq (occurrence of parental types) greater than 50% indicates that genes are linked (on same chromosome) |
|
|
Linked genes |
Genes that are located on the same chromosome inherited together Each chromosome has hundreds or thousands of genes (except Y) |
|
|
The crosses of linked genes differ from those expected according to... |
Law of independent assortment Dihybrid cross of genes inherited together on same chromosome=offspring phenotype is 3:1 Dihybrid cross of genes located on separate chromosomes= offspring phenotype is 9:3:3:1 |
|
|
Parental types |
Offspring with a phenotype matching one of the parental phenotype |
|
|
Recombinant type or recombinants |
Offspring with no parental phenotypes (new combinations of traits) |
|
|
Nonparental phenotypes |

Involves genetic recombination (combination of traits differing from either parent) Max of 50% freq of recombination is observed for any two genes on different (nonhomologous) chromosomes |
|
|
Nonparental phenotypes |
Involves genetic recombination (combination of traits differing from either parent) Max of 50% freq of recombination is observed for any two genes on different (nonhomologous) chromosomes |
|
|
Recombination of unlinked genes: independent assortment of chromosomes |
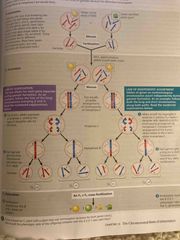
Physical basis of recombination btw unlinked genes is the random orientation of homologous chromosomes at metaphase I of meiosis This leads to the independent assortment of alleles The F1 parent (YyRr) produces 4 gametes with 4 different combos of alleles: YR, Yr, yR, yr |
|
|
Recombination of unlinked genes: independent assortment of chromosomes |
Physical basis of recombination btw unlinked genes is the random orientation of homologous chromosomes at metaphase I of meiosis This leads to the independent assortment of alleles The F1 parent (YyRr) produces 4 gametes with 4 different combos of alleles: YR, Yr, yR, yr |
|
|
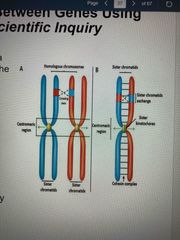
Crossing over and linked genes |
While some genes are linked, nonoarental allele combos are still produced as a result of crossing over The physical connection btw genes on same chromosome is broken by crossing over |
|
|
New combos of alleles and natural selection |
Recombinant chromosomes bring alleles together in new combinations in gametes Random fertilization increases even further variations produced If these traits are better suited for the environment, organisms will succeed and continue to pass on those genes |
|
|
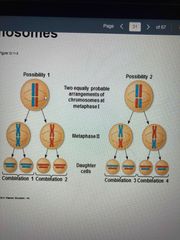
Nondisjunction |
Pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate during meiosis I or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II Result=one gamete receives 2 of same type of chromosome and other receives none |
|
|
Aneuploidy |
Offspring with this condition have an abnormal number of a particular chromosome Results from fertilization of gametes where nondisjunction occurred |
|
|
Monosomic zygote |
Has only one copy of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Trisomic zygote |
Three copies of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Monosomy and trisomy are estimated to occur in btw.. |
10 and 25% of human conceptions |
|
|
Polyploidy |
A condition in which an organism has more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes Commons in plants More normal in appearance than aneuploids |
|
|
Triploidy |
3n is 3 sets of chromosomes Normal gamete fertilizes a diploid gamete produced by nondisjunction of all its chromosomes |
|
|
Tetraploidy |
4n is 4 sets of chromosomes 2n zygote fails to divide after replicating its chromosomes |
|
|
Genetic map |
An ordered list of genetic loci along a chromosome Created by Alfred sturtevant (student of Morgan) |
|
|
Sturtevant hypothesized... |
Percentage of recombinant offspring depends on distant btw genes on chromosome Crossing over is random and can occur at any point on the chromosome |
|
|
The further apart two genes are, the higher the probability that... |
A crossover will occur btw them Therefore, the higher the recombination freq |
|
|
Linkage map |
Genetic map of a chromosome based on recombination frequencies Provides an approximate picture of a chromosome |
|
|
Map units |
Distance btw genes One map unit (centimorgan) represents a 1% recombination frequency |
|
|
Map unit indidcate relative distance and order, not |
Precise locations of genes |
|
|
Genes that are far apart i the same chromosome... |
Have a recombination frequency of 50% and behave as if found on separate chromosome Physically linked but not genetically linked |
|
|
Combining linkage maps with other methods like chromosomal banding, geneticists can develop... |
Cytogenetic maps of chromosomes Indicate position of genes due to chromosomal features Ultimate maps show physical distance btw gene loci in DNA |
|
|
Alterations of chromosome number or structure cause genetic disorders |
Physical and chemical disturbances, errors during meiosis lead to damage of chromosomes or change the number Large-scale alterations can lead to abortions or cause developmental disorders Plants tolerate such genetic changes better |
|
|
New combos of alleles and natural selection |
Recombinant chromosomes bring alleles together in new combinations in gametes Random fertilization increases even further variations produced If these traits are better suited for the environment, organisms will succeed and continue to pass on those genes |
|
|
Nondisjunction |
Pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate during meiosis I or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II Result=one gamete receives 2 of same type of chromosome and other receives none |
|
|
Aneuploidy |
Offspring with this condition have an abnormal number of a particular chromosome Results from fertilization of gametes where nondisjunction occurred |
|
|
Monosomic zygote |
Has only one copy of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Trisomic zygote |
Three copies of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Monosomy and trisomy are estimated to occur in btw.. |
10 and 25% of human conceptions |
|
|
Polyploidy |
A condition in which an organism has more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes Commons in plants More normal in appearance than aneuploids |
|
|
Triploidy |
3n is 3 sets of chromosomes Normal gamete fertilizes a diploid gamete produced by nondisjunction of all its chromosomes |
|
|
Tetraploidy |
4n is 4 sets of chromosomes 2n zygote fails to divide after replicating its chromosomes |
|
|
Disorders created by chromosomal alterations |
Freq of aneuploid zygotes is high in humans, most lead to abortion Some types impact than others Those who survive have a set of symptoms or syndrome, characteristic of the type of aneuploidy |
|
|
Deletion |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Removes a chromosomal segment |
|
|
Genetic map |
An ordered list of genetic loci along a chromosome Created by Alfred sturtevant (student of Morgan) |
|
|
Duplication |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Repeats a segment |
|
|
Inversion |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Reverses orientation of a segment within a chromosome |
|
|
Translocation |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Moves a segment from one chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome Typical harmful |
|
|
Duplications and translocations are |
Harmful |
|
|
A diploid embryo that is homozygous for a large deletion or a Mae with a large deletion to its single X chromosome.. |
Usually missing many essential genes Usually lethal |
|
|
Reciprocal translocations or inversions can alter... |
Phenotype bc genes expression is influenced by its location among neighboring genes |
|
|
Sturtevant hypothesized... |
Percentage of recombinant offspring depends on distant btw genes on chromosome Crossing over is random and can occur at any point on the chromosome |
|
|
The further apart two genes are, the higher the probability that... |
A crossover will occur btw them Therefore, the higher the recombination freq |
|
|
Linkage map |
Genetic map of a chromosome based on recombination frequencies Provides an approximate picture of a chromosome |
|
|
Map units |
Distance btw genes One map unit (centimorgan) represents a 1% recombination frequency |
|
|
Map unit indidcate relative distance and order, not |
Precise locations of genes |
|
|
Genes that are far apart i the same chromosome... |
Have a recombination frequency of 50% and behave as if found on separate chromosome Physically linked but not genetically linked |
|
|
Combining linkage maps with other methods like chromosomal banding, geneticists can develop... |
Cytogenetic maps of chromosomes Indicate position of genes due to chromosomal features Ultimate maps show physical distance btw gene loci in DNA |
|
|
Alterations of chromosome number or structure cause genetic disorders |
Physical and chemical disturbances, errors during meiosis lead to damage of chromosomes or change the number Large-scale alterations can lead to abortions or cause developmental disorders Plants tolerate such genetic changes better |
|
|
New combos of alleles and natural selection |
Recombinant chromosomes bring alleles together in new combinations in gametes Random fertilization increases even further variations produced If these traits are better suited for the environment, organisms will succeed and continue to pass on those genes |
|
|
Nondisjunction |
Pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate during meiosis I or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II Result=one gamete receives 2 of same type of chromosome and other receives none |
|
|
Aneuploidy |
Offspring with this condition have an abnormal number of a particular chromosome Results from fertilization of gametes where nondisjunction occurred |
|
|
Monosomic zygote |
Has only one copy of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Trisomic zygote |
Three copies of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Monosomy and trisomy are estimated to occur in btw.. |
10 and 25% of human conceptions |
|
|
Polyploidy |
A condition in which an organism has more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes Commons in plants More normal in appearance than aneuploids |
|
|
Triploidy |
3n is 3 sets of chromosomes Normal gamete fertilizes a diploid gamete produced by nondisjunction of all its chromosomes |
|
|
Tetraploidy |
4n is 4 sets of chromosomes 2n zygote fails to divide after replicating its chromosomes |
|
|
Disorders created by chromosomal alterations |
Freq of aneuploid zygotes is high in humans, most lead to abortion Some types impact than others Those who survive have a set of symptoms or syndrome, characteristic of the type of aneuploidy |
|
|
Deletion |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Removes a chromosomal segment |
|
|
Genetic map |
An ordered list of genetic loci along a chromosome Created by Alfred sturtevant (student of Morgan) |
|
|
Duplication |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Repeats a segment |
|
|
Inversion |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Reverses orientation of a segment within a chromosome |
|
|
Translocation |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Moves a segment from one chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome Typical harmful |
|
|
Duplications and translocations are |
Harmful |
|
|
A diploid embryo that is homozygous for a large deletion or a Mae with a large deletion to its single X chromosome.. |
Usually missing many essential genes Usually lethal |
|
|
Reciprocal translocations or inversions can alter... |
Phenotype bc genes expression is influenced by its location among neighboring genes |
|
|
Sturtevant hypothesized... |
Percentage of recombinant offspring depends on distant btw genes on chromosome Crossing over is random and can occur at any point on the chromosome |
|
|
The further apart two genes are, the higher the probability that... |
A crossover will occur btw them Therefore, the higher the recombination freq |
|
|
Linkage map |
Genetic map of a chromosome based on recombination frequencies Provides an approximate picture of a chromosome |
|
|
Map units |
Distance btw genes One map unit (centimorgan) represents a 1% recombination frequency |
|
|
Map unit indidcate relative distance and order, not |
Precise locations of genes |
|
|
Genes that are far apart i the same chromosome... |
Have a recombination frequency of 50% and behave as if found on separate chromosome Physically linked but not genetically linked |
|
|
Combining linkage maps with other methods like chromosomal banding, geneticists can develop... |
Cytogenetic maps of chromosomes Indicate position of genes due to chromosomal features Ultimate maps show physical distance btw gene loci in DNA |
|
|
Alterations of chromosome number or structure cause genetic disorders |
Physical and chemical disturbances, errors during meiosis lead to damage of chromosomes or change the number Large-scale alterations can lead to abortions or cause developmental disorders Plants tolerate such genetic changes better |
|
|
New combos of alleles and natural selection |
Recombinant chromosomes bring alleles together in new combinations in gametes Random fertilization increases even further variations produced If these traits are better suited for the environment, organisms will succeed and continue to pass on those genes |
|
|
Nondisjunction |
Pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate during meiosis I or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II Result=one gamete receives 2 of same type of chromosome and other receives none |
|
|
Aneuploidy |
Offspring with this condition have an abnormal number of a particular chromosome Results from fertilization of gametes where nondisjunction occurred |
|
|
Monosomic zygote |
Has only one copy of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Trisomic zygote |
Three copies of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Monosomy and trisomy are estimated to occur in btw.. |
10 and 25% of human conceptions |
|
|
Polyploidy |
A condition in which an organism has more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes Commons in plants More normal in appearance than aneuploids |
|
|
Triploidy |
3n is 3 sets of chromosomes Normal gamete fertilizes a diploid gamete produced by nondisjunction of all its chromosomes |
|
|
Tetraploidy |
4n is 4 sets of chromosomes 2n zygote fails to divide after replicating its chromosomes |
|
|
Disorders created by chromosomal alterations |
Freq of aneuploid zygotes is high in humans, most lead to abortion Some types impact than others Those who survive have a set of symptoms or syndrome, characteristic of the type of aneuploidy |
|
|
Deletion |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Removes a chromosomal segment |
|
|
Genetic map |
An ordered list of genetic loci along a chromosome Created by Alfred sturtevant (student of Morgan) |
|
|
Duplication |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Repeats a segment |
|
|
Inversion |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Reverses orientation of a segment within a chromosome |
|
|
Translocation |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Moves a segment from one chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome Typical harmful |
|
|
Duplications and translocations are |
Harmful |
|
|
A diploid embryo that is homozygous for a large deletion or a Mae with a large deletion to its single X chromosome.. |
Usually missing many essential genes Usually lethal |
|
|
Reciprocal translocations or inversions can alter... |
Phenotype bc genes expression is influenced by its location among neighboring genes |
|
|
Down’s syndrome |
Aneuploid condition with 3 copies of chromosome 21 It effects 1 out of every 830 Facial features, heart defects, developmental delays, susceptible to respiratory infections and Alzheimer’s Born mostly sterile (natural selection) |
|
|
XXX females and XYY males |
Nondisjunction of sex chromosomes Females: healthy, no unusual physical features Males: taller, healthy |
|
|
Klinefelter syndrome |
Nondisjunction of sex chromosomes Result of an extra X in males-XXY Male sex organs but testes unusually small and sterile Some breast enlargement and other female characteristics |
|
|
Monosomy X or Turner syndrome |
XO females who are sterile Only known viable monosomy in humans |
|
|
Sturtevant hypothesized... |
Percentage of recombinant offspring depends on distant btw genes on chromosome Crossing over is random and can occur at any point on the chromosome |
|
|
Cri du chat (cry of the cat) |
Deletion of chromosome 5 Severely developmental delays, catlike cry Usually die in infancy |
|
|
Chronic myelohenous leukemia |
Translocation of chromosome 22 and 9 Philadelphia chromosome |
|
|
The further apart two genes are, the higher the probability that... |
A crossover will occur btw them Therefore, the higher the recombination freq |
|
|
Linkage map |
Genetic map of a chromosome based on recombination frequencies Provides an approximate picture of a chromosome |
|
|
Map units |
Distance btw genes One map unit (centimorgan) represents a 1% recombination frequency |
|
|
Map unit indidcate relative distance and order, not |
Precise locations of genes |
|
|
Genes that are far apart i the same chromosome... |
Have a recombination frequency of 50% and behave as if found on separate chromosome Physically linked but not genetically linked |
|
|
Combining linkage maps with other methods like chromosomal banding, geneticists can develop... |
Cytogenetic maps of chromosomes Indicate position of genes due to chromosomal features Ultimate maps show physical distance btw gene loci in DNA |
|
|
Alterations of chromosome number or structure cause genetic disorders |
Physical and chemical disturbances, errors during meiosis lead to damage of chromosomes or change the number Large-scale alterations can lead to abortions or cause developmental disorders Plants tolerate such genetic changes better |
|
|
New combos of alleles and natural selection |
Recombinant chromosomes bring alleles together in new combinations in gametes Random fertilization increases even further variations produced If these traits are better suited for the environment, organisms will succeed and continue to pass on those genes |
|
|
Nondisjunction |
Pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate during meiosis I or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II Result=one gamete receives 2 of same type of chromosome and other receives none |
|
|
Sturtevant hypothesized... |
Percentage of recombinant offspring depends on distant btw genes on chromosome Crossing over is random and can occur at any point on the chromosome |
|
|
The further apart two genes are, the higher the probability that... |

A crossover will occur btw them Therefore, the higher the recombination freq |
|
|
Linkage map |

Genetic map of a chromosome based on recombination frequencies Provides an approximate picture of a chromosome |
|
|
Monosomy and trisomy are estimated to occur in btw.. |
10 and 25% of human conceptions |
|
|
Polyploidy |
A condition in which an organism has more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes Commons in plants More normal in appearance than aneuploids |
|
|
Triploidy |
3n is 3 sets of chromosomes Normal gamete fertilizes a diploid gamete produced by nondisjunction of all its chromosomes |
|
|
Tetraploidy |
4n is 4 sets of chromosomes 2n zygote fails to divide after replicating its chromosomes |
|
|
Disorders created by chromosomal alterations |
Freq of aneuploid zygotes is high in humans, most lead to abortion Some types impact than others Those who survive have a set of symptoms or syndrome, characteristic of the type of aneuploidy |
|
|
Nondisjunction |
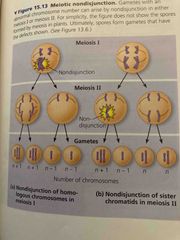
Pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate during meiosis I or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II Result=one gamete receives 2 of same type of chromosome and other receives none |
|
|
Aneuploidy |
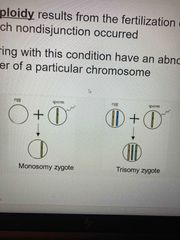
Offspring with this condition have an abnormal number of a particular chromosome Results from fertilization of gametes where nondisjunction occurred |
|
|
Monosomic zygote |

Has only one copy of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Trisomic zygote |

Three copies of a particular chromosome |
|
|
Translocation |
Type of chromosome structure breakage Moves a segment from one chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome Typical harmful |
|
|
Duplications and translocations are |
Harmful |
|
|
A diploid embryo that is homozygous for a large deletion or a Mae with a large deletion to its single X chromosome.. |
Usually missing many essential genes Usually lethal |
|
|
Reciprocal translocations or inversions can alter... |
Phenotype bc genes expression is influenced by its location among neighboring genes |
|
|
Down’s syndrome |
Aneuploid condition with 3 copies of chromosome 21 It effects 1 out of every 830 Facial features, heart defects, developmental delays, susceptible to respiratory infections and Alzheimer’s Born mostly sterile (natural selection) |
|
|
Deletion |

Type of chromosome structure breakage Removes a chromosomal segment |
|
|
Duplication |

Type of chromosome structure breakage Repeats a segment |
|
|
Inversion |
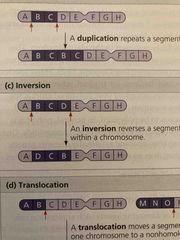
Type of chromosome structure breakage Reverses orientation of a segment within a chromosome |
|
|
Translocation |

Type of chromosome structure breakage Moves a segment from one chromosome to a nonhomologous chromosome Typical harmful |
|
|
Cri du chat (cry of the cat) |
Deletion of chromosome 5 Severely developmental delays, catlike cry Usually die in infancy |
|
|
Chronic myelohenous leukemia |
Translocation of chromosome 22 and 9 Philadelphia chromosome |
|
|
The further apart two genes are, the higher the probability that... |
A crossover will occur btw them Therefore, the higher the recombination freq |
|
|
Linkage map |
Genetic map of a chromosome based on recombination frequencies Provides an approximate picture of a chromosome |
|
|
Map units |
Distance btw genes One map unit (centimorgan) represents a 1% recombination frequency |
|
|
Map unit indidcate relative distance and order, not |
Precise locations of genes |
|
|
Genes that are far apart i the same chromosome... |
Have a recombination frequency of 50% and behave as if found on separate chromosome Physically linked but not genetically linked |
|
|
Combining linkage maps with other methods like chromosomal banding, geneticists can develop... |
Cytogenetic maps of chromosomes Indicate position of genes due to chromosomal features Ultimate maps show physical distance btw gene loci in DNA |
|
|
Chronic myelohenous leukemia |
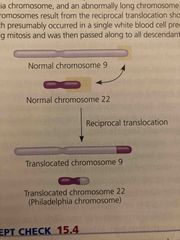
Translocation of chromosome 22 and 9 Philadelphia chromosome |
|
|
Exceptions to Mendelian rule |
One is inside nucleus: genomic imprinting One is outside nucleus: extranuclear genes Sex of parent contributing an allele is a factor |
|
|
Genomic imprinting |
Phenotype depends on which parent passed along the trait Involves silencing of certain genes Involves autosomes Over 60 imprinted genes identified |
|
|
When does genomic imprinting occur? |
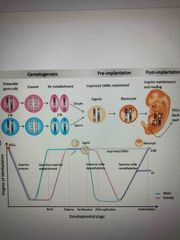
During gamete formation In each generation, old imprints are erased Bc genes are imprinted differently in sperm and ova, a zygote expresses only one allele of an imprinted gene inherited either from the female or male |
|
|
Genomic imprinting for insulin-like growth factor 2 in mice |
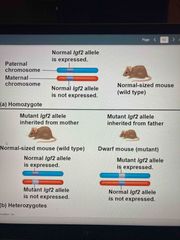
Only paternal allele is expressed Alllele is imprinted in eggs turning off expression of the imprinted allele In sperm, not imprinted and functions normally |
|
|
Imprinting and methylation |
Methylation silences an allele Heavily methylated genes are usually inactive |
|
|
Extranuclear genes (cytoplasmic) |
Found in organelles in the cytoplasm Mitochondria, chloroplasts, and other plant plastids carry small circular DNA molecules Extranuclear genes are inherited maternally bc the zygotes cytoplasm comes from the egg |
|
|
First evidence of extranuclear genes |
Inheritance of yellow and white patches on leaves of an otherwise green plant |
|
|
All mitochondrial genes are |
Maternal inheritance Some defects prevent cells from making enough ATP and affect muscular and nervous system Mitochondrial mutations occur in normal aging process
|
|
|
Mitochondrial myopathy and lebers hereditary optic neuropathy |
Affect oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
To avoid mitochondrial disorders |
Chromosomes from egg of an affected mother could be transferred to an egg of a healthy donor-two mother egg Fertilized by sperm and then transplanted to womb of prospective mother |

